doi: 10.62486/agmu202314
ORIGINAL
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in human talent management
Beneficios de la Inteligencia Artificial en la gestión del talento humano
Julio Cesar Gama Espinosa1
![]() *, Lina María Leiva Sánchez1
*, Lina María Leiva Sánchez1
![]() *, Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira1
*, Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira1
![]() *
*
1Corporación Universitaria Nacional de Educación Superior. Bogotá, Colombia.
Cite as: Gama Espinosa JC, Leiva Sánchez LM, Fajardo Pereira MA. Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in human talent management. Multidisciplinar (Montevideo). 2023; 1:14. https://doi.org/10.62486/agmu202314
Submitted: 01-08-2023 Revised: 19-10-2023 Accepted: 20-12-2023 Published: 21-12-2023
Editor: Prof.
Dr. Javier González Argote ![]()
ABSTRACT
Human talent and artificial intelligence have been closely related, having a great impact on the performance and productivity of today’s organizations. In this research work, we sought to identify the challenges posed by the implementation of artificial intelligence tools in human talent management, such as data privacy, discrimination and automated decision making, through the review of scientific literature, this as the main objective. To develop it, sources of research articles, magazines and previous research carried out on the topic in the last ten years were used, with which it was possible to identify the use of AI for the selection and retention of human talent, the development of skills and skills, in addition to benefiting the well-being of collaborators; but also disadvantages such as its impact on privacy and the growing concern about job replacement. Concluding, to take full advantage of the benefits and minimize the problems associated with AI in human talent, it is necessary to have clear and transparent regulations, encouraging collaboration and development of knowledge in employees and ensuring ethics in the use of AI. within the organization.
Keywords: Automation; Evolution; Skills; Technology; Transformation.
RESUMEN
El talento humano (TH) y la inteligencia artificial (IA) han estado estrechamente relacionados teniendo un gran impacto en el rendimiento y la productividad de las organizaciones actuales. En este artículo, se buscó identificar los retos que plantea la implementación de herramientas de inteligencia artificial en la gestión de talento humano, tales como la privacidad de los datos, la discriminación y la toma de decisiones automatizada, a través de la revisión de la literatura científica, esto como objetivo principal. Para desarrollarlo, se utilizaron fuentes de artículos de investigación, revistas e investigaciones anteriores realizadas sobre el tema en los últimos diez años, con lo que se pudo identificar el uso de la IA para la selección y retención del talento humano, el desarrollo de habilidades y competencias, además de beneficiar al bienestar de los colaboradores; pero también desventajas como su impacto en la privacidad y la creciente preocupación por el reemplazo de trabajos. Concluyendo, que para aprovechar al máximo los beneficios y minimizar los problemas asociados con la IA en el talento humano, es necesario tener regulaciones claras y transparentes, fomentando la colaboración y desarrollo de conocimientos en los empleados y asegurando la ética en el uso de la IA dentro de la organización.
Palabras clave: Automatización; Evolución; Habilidades; Tecnología; Transformación.
INTRODUCTION
The convergence between artificial intelligence (AI) and human capital has attracted significant interest in contemporary business.(1,2,3,4,5) has been defined as the ability of machines to execute tasks that would typically require human intervention, is intertwined with the concept of human capital that encompasses the skills, knowledge, and experiences contributed by individuals in an organization.(6,7,8,9,10,11) This complex intertwining establishes an essential starting point for exploring how AI and human capital interact and influence each other.(12,13,14,15,16)
Several approaches have been delineated in the current scientific literature that shed light on the dynamics between artificial intelligence and human capital.(17,18,19,20,21) These approaches, based on digital transformation, machine learning, talent management, diversity, and decision-making, offer valuable insights into how these two forces converge and affect the business domain.(22,23,24,25,26)
Despite the advances and opportunities afforded by this convergence, crucial issues emerge in implementing artificial intelligence in enterprises’ human capital context.(27,28,29,30,31) These issues include resistance to change, the skills gap, ethical issues in decision-making, data privacy, and the need for effective change management.(32,33,34,35,36) These fundamental challenges frame the complex landscape that organizations must address to fully capitalize on the benefits of AI in the workplace.(37,38,39,40,41)
In the specific context of companies in Colombia, these issues take on particular nuances.(42,43,44) Cultural dynamics, evolving technological infrastructures, and government regulations complicate artificial intelligence and human capital intersection.(45,46,47,48) Understanding these specific issues is essential to addressing the challenges in implementing AI and optimizing human capital in the Colombian context.(49,50,51,52,53)
This analysis seeks to contrast the issues identified in the scientific literature with the contextual reality of companies in Colombia. This comparison aims to offer a comprehensive view of the challenges organizations face when integrating artificial intelligence and managing their human capital in a constantly evolving Colombian business context.
METHOD
The methodological design is descriptive, a product of documentary reviews and research, developed under qualitative approaches, which allowed the investigation of the topic raised on the benefits of artificial intelligence in the management of human talent in organizations, allowing different authors to intervene in the description of the analyzed topic.
The documentary review and research were carried out from the bibliographic search in theses, articles, books, and scientific publications in journals indexed in the SCOPUS Elsevier database.
The information presented in this article was carried out in the following phases:
· In the exploratory phase, a search of several documents related to the research topic was carried out in the Scopus Elsevier database using the keywords “human talent management” or “human talent” or “human capital “OR firm or business.
· In the selection phase, a detailed analysis of the information gathered from the different sources consulted was generated; in this way, only the information that had a direct relationship with the research topic was taken, and the open-access literature in Spanish and English was reviewed. A total of 53 documents were obtained from the search.
· In the results phase, the information obtained was downloaded in CSV format. The analysis was initially carried out in Excel format. Vosviewer software was used to analyze publication trends and the most important topics.
The document was formed from research and scientific journals during the first phase; in the second phase, as mentioned above, the relevant information was taken to complement the document. Finally, coherence was generated, and the information was joined reasonably to consolidate the document.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into business management revolutionizes how organizations operate and make strategic decisions.(54,55,56,57,58) AI, with its ability to analyze large volumes of data and generate valuable insights, is transforming performance management, career development, human resource (HR) management, and workforce planning.(59)
The main field of application of artificial intelligence is developing human talent in companies
From performance management, AI offers tools for predictive analytics, allowing organizations to anticipate future trends and behaviors. This predictive capability is crucial to identify areas for improvement and suggest actions for employees’ professional development.(60,61) AI algorithms can analyze historical performance and, through predictive models, identify patterns that suggest specific competencies or skills that need to be developed.(62,63)
In addition, AI facilitates the implementation of continuous feedback systems.(64) These platforms can offer real-time job performance assessments, providing employees and managers with valuable information for immediate adjustments.(65,66) AI-based feedback can be more objective and specific, contributing to a more productive and motivating work environment.(67,68)
Regarding professional development, AI is crucial in personalizing learning and training.(69,70,71) AI-based systems can analyze employee profiles to suggest customized training and development programs.(72,73) This personalization ensures that employees receive relevant and practical training, which improves their skills and, thus, their job performance.(74,75)
Concerning human resource management, AI contributes significantly to the automation of administrative tasks. For example, it can handle personnel selection processes and filter candidates based on pre-established criteria, which saves time and resources.(76) In addition, these technologies can help eliminate unconscious biases in the hiring process, promoting a more diverse and inclusive workforce.(77)
Another exciting application of AI in HR is sentiment analysis.(78) AI-based tools can assess employee emotional well-being through surveys and feedback, providing managers with valuable information to improve work climate and employee satisfaction.(79)
In workforce planning, AI-based predictive models are instrumental. These models can forecast an organization’s future staffing needs, aiding in hiring planning and capacity management.(80) For example, they can predict the demand for specific skills and competencies in the marketplace, allowing the company to anticipate and prepare accordingly.(81)
Finally, AI plays a crucial role in organizational culture and collaborative data analysis.(82) By analyzing team communications and interactions, AI can assess organizational culture’s health and suggest areas for improvement. This includes identifying effective communication patterns, team collaboration, and employee engagement and satisfaction.(83)
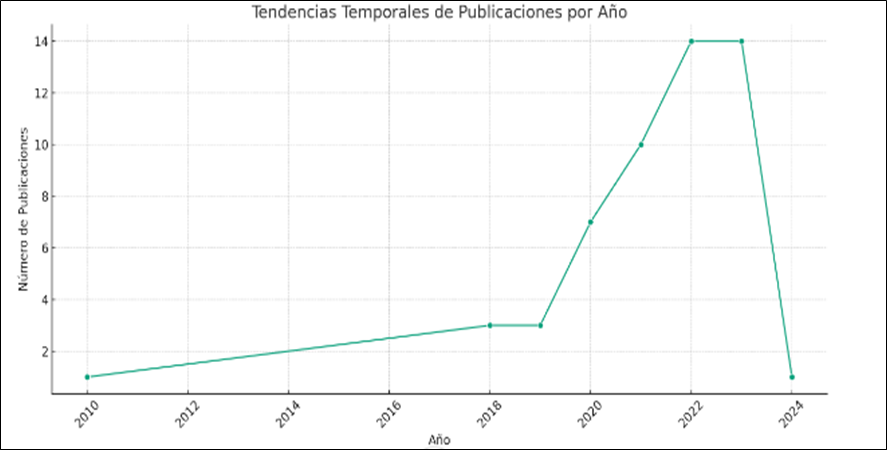
Figure 1. Number of AI and human capital related publications from 2010-2024
Note: the figure shows the number of academic publications per year.
Each point represents a specific year, and the line connects these points to show the trend over time. You can see how the number of publications has fluctuated over the years. A significant increase in recent years due to the worldwide interest in the use of AI in business and the improvement of business conditions.

Figure 2. Keywords related to AI and human capital
Note: the figure shows the most frequent terms in the titles.
The more extensive terms represent words or topics that appear more frequently, which provides a quick overview of the predominant themes in the literature you are analyzing. This analysis helps to quickly identify key focus areas and popular topics in your dataset. This highlights human capital, artificial intelligence digitization, productivity, technologies, development, and research.(84)
|
Table 1. Most representative authors in AI and human talent in the periods 2010-2024 |
|||
|
Article |
Authors |
Quotations |
Year of Publication |
|
Influences of the industry 4.0 revolution on the economy and society |
Sima V.; Gheorghe I.G.; Subić J.; Nancu D. |
263 |
2020 |
|
The Challenges and Opportunities in the Digital Era: Smart E-Tourism |
Almeida F.; Duarte Santos J.; Augusto Monteiro J. |
202 |
2020 |
|
Auditing in times of social distancing: the effects of COVID-19 on auditing quality |
Albitar K.; Gerged A.M.; Kikhia H.; Hussainey K. |
87 |
2021 |
|
Rebooting employees: upskilling for artificial intelligence in enterprises |
Jaiswal A.; Arun C.J.; Varma A. |
62 |
2022 |
|
The risks of digitalization and the adaptation of regional labor markets in Russia |
Zemtsov S.; Barinova V.; Semenova R. |
48 |
2019 |
|
A review paper on artificial intelligence at the edge |
Berhil S.; Benlahmar H.; Labani N. |
43 |
2019 |
|
Knowledge investments, business R&D and innovation success |
van Hemert P.; Nijkamp P. |
38 |
2010 |
|
Relationships among healthcare digitalization, social capital, and supply chain performance |
Kim H.K.; Lee C.W. |
34 |
2021 |
|
Amenity proximity analysis for sustainable brownfield development |
Beames A.; Broekx S.; Schneidewind U.; Landuyt D.; Others |
23 |
2018 |
|
Note: the table lists the most representative authors of AI and human capital publications published in the Scopus database Elsevier. It was constructed from the visibility factor of several citations. |
|||
Of particular note is the research by Sima et al.(86) entitled “Influences of the Industry 4.0 Revolution on the Economy and Society.” This group of authors has made a remarkable contribution by exploring the impacts of the Industry 4.0 revolution. Their work focuses on how this revolution affects human capital development and consumer behavior, a crucial issue in digitization and automation.(85)
In “The Challenges and Opportunities in the Digital Era: Smart E-Tourism,” their study addresses the challenges and opportunities of digitalization in the tourism industry. This sector is constantly evolving thanks to technology.(86) Albitar et al.(8) “Auditing in times of social distancing: the effects of COVID-19 on auditing quality”: This team has investigated how the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted audit quality, a fundamental aspect in the financial and business world, especially relevant in the context of recent global changes. His contribution arises from the use of AI tools that are used in financial auditing processes, which allow for predicting possible fraud in organizations.(87)
On the other hand, the study by Jaiswal et al.(55) in “Rebooting Employees: Upskilling for Artificial Intelligence in Enterprises” Focuses on the importance of training and skills development in artificial intelligence for employees in enterprises.(88) Their research highlights the need to adapt the workforce to emerging technologies. In the same vein, Zemtsov et al.(103), in “The Risks of Digitalization and the Adaptation of Regional Labor Markets in Russia,” have explored the risks associated with digitalization and how it affects regional labor markets in Russia, an essential study for understanding the impact of technology in different geographic and economic contexts.(89)
On the other hand, Berhil et al.(31), in “A Review Paper on Artificial Intelligence at the Edge,” have focused on AI in edge computing. This fast-growing area combines artificial intelligence with telecommunications networks and data processing at the network’s edge. Likewise, Van Hemert et al.(91) investigated the relationship between knowledge investments, business R&D, and innovation success, providing a valuable tool for developing R&D-based business strategies.(90)
On the other hand, Kim et al.(62) in “Relationships among Healthcare Digitalization, Social Capital, and Supply Chain Performance” have studied how digitalization in the healthcare sector relates to social capital and supply chain performance, a critical area in global healthcare and supply chain management. Beames et al.(27), in their paper “Amenity proximity analysis for sustainable brownfield development,”: this team has focused on amenity proximity analysis for sustainable brownfield development, an essential aspect of urban planning and sustainable development.(92,93)
Focus on related studies in the academic literature associated with artificial intelligence and human talent
The topics related to AI are becoming more and more permanent in studies worldwide. There are more and more applications of AI in the business field worldwide.(94)
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
This topic is one of the most prominent, which is unsurprising given its growing importance in various fields. Artificial intelligence frequently appears in studies on technology, ethics, impact on society and business, and the development of new applications.
These authors have contributed to understanding AI in various contexts, from its practical applications to ethical and social considerations.(95)
Digitization
This topic covers digital transformation and its impact on healthcare, education, and industry sectors. Studies focus on how digitalization changes traditional operations and creates new opportunities and challenges. Authors have explored how digitalization is reshaping industries and societies. They focus on digital transformation and its impact on different sectors.(96)
Human Capital Development
This approach relates to the impact of technology and innovation on developing skills and competencies. Studies here focus on education, training, and workforce preparation for the digital era. Authors have investigated the impact of technology and innovation on the development of skills and competencies, highlighting the importance of adapting the workforce to the digital age.(97)
Economic and Social Impact
This theme discusses how technological advances, especially artificial intelligence and digitization, redefine the economic and social landscape. It includes studies on the influence on consumer behavior, labor market dynamics, and business ethics. Economic and Social Impact: Although this theme is cross-cutting and may include several authors from the other approaches, especially those focused on artificial intelligence and digitization.(98)
Sustainability and Urban Development
This approach focuses on sustainability in the context of urban planning and development. Studies address issues such as sustainable development and efficient resource management in the context of urbanization and digitalization. Sustainability and Urban Development: Similar to the previous case, this approach may be implicit in several works related to digitization and AI.(99)
Figure 3 shows the different themes highlighted according to the frequency of keywords used.
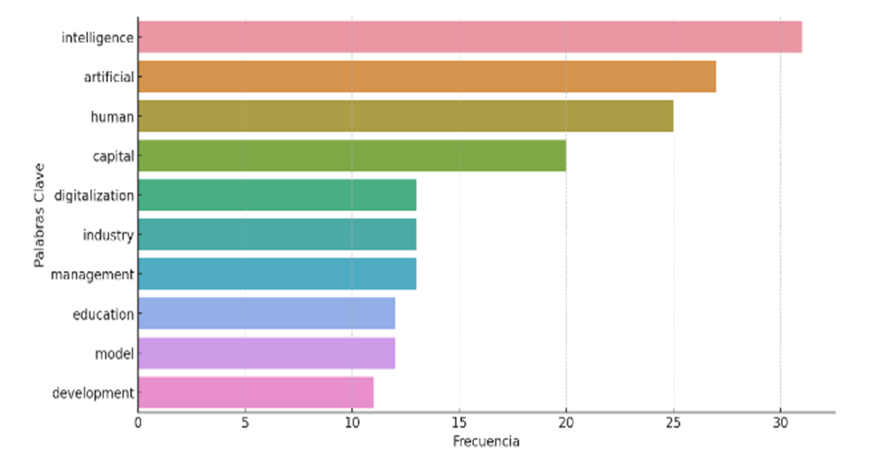
Figure 3. Themes highlighted by frequency of keywords
Note: the figure shows the topics addressed about AI and human talent. The main focuses of each study are highlighted. Its construction is based on the abstracts of the Scopus database Elsevier.
In academia, several key terms and authors stand out for their contribution to specific topics. For example, Intelligence, which encompasses both artificial and human Intelligence, has been an area of focus for authors such as Aldhyani et al.(11) and Matute-Pinos et al.(75), who have explored its multiple applications and theories. On the other hand, the subject of artificial Intelligence focuses mainly on its influence on technology, ethics, society, and business. This field has been notably enriched by the work of authors Artemenko et al.(23).(100,101,102)
As for the term Human, it is related to studies on human behavior, Development, and capabilities. Authors have contributed significantly to this field, offering new perspectives and discoveries. Management, which encompasses administration and Management in sectors such as business, technology, and Education, has been addressed by AlQershi N., Ramayah T., and Panchenko V. These authors have provided valuable insights and management strategies adapted to contemporary challenges.(103)
Focusing on educational processes, methodologies, and teaching technologies is a crucial study area. To develop innovative and effective educational practices for Kuzior(66). Model refers to using theoretical or computational models to simulate and understand systems or processes in various disciplines. Authors have been instrumental in this field, providing models that help to better understand complex phenomena.(104)
Finally, Development, which addresses growth and progress in areas such as urban, technological, and social Development, has been explored by authors such as Kuzior A., Heijungs R., and Migliaccio K. Their research has been crucial to understanding development patterns and their impact on society. Each of these topics and authors represents an essential component of the tapestry of contemporary research, contributing to the evolution of knowledge in their respective fields.(105)

Figure 4. Box plot by keyword quartile frequency
Figure 4 shows the frequency distribution of the 10 most frequent keywords in the publications in your database. Each box represents the frequency distribution of a specific keyword in all publications. In this graph, the center line of each box indicates the median frequency, while the ends represent the first and third quartiles. Vertical lines (or “whiskers”) extend to the minimum and maximum values within a reasonable range, and points outside these whiskers indicate outliers.
CONCLUSIONS
This paper highlights the importance of integrating artificial intelligence into human talent management in companies. AI offers tools to improve talent selection and retention, skills and competency development, and employee well-being. However, significant challenges, such as resistance to change, the skills gap, ethical issues in decision-making, and data privacy, are also identified.
To minimize the problems associated with AI in privacy and discrimination, transparency and accountability measures in decision-making must be implemented. In addition, precise and effective regulations should be developed to ensure AI’s ethical and responsible use in the workplace.
In terms of possible future research trends, AI’s effects on organizational culture and team collaboration can be further explored. The implications of AI on diversity management and inclusion in the workplace can also be investigated. In addition, comparative studies can be developed across different countries and regions to identify best practices in implementing AI in human talent management.
REFERENCES
1. Leon E, Rodriguez C, Martínez MDC, Ron M. Hearing injuries due to atmospheric pressure changes in air and water survival training instructors. Health Leadership and Quality of Life 2023;2:39-39. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl202339.
2. Suárez EJC. Cursos de calidad para una educación superior virtual de calidad. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias 2023;2:575-575. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2023575.
3. Viera EJH, Meléndez NMN, Claudio MCM, Ruiz JAZ. Selection process in the Operations area of a company in the ecological sector. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:13-13. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa202313.
4. Abdullah M, Ahmed ZAT, Alsubari SN, Aldhyani THH, Almaaytah SA. Application of Artificial Intelligence for Better Investment in Human Capital. Mathematics. 2023;11(3):1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030612.
5. Peña MG, Ocmin LSL, Romero-Carazas R. Control interno de inventario y la gestión de resultados de un emporio comercial de la región de San Martín - Perú. Región Científica 2023;2:202392-202392. https://doi.org/10.58763/rc202392.
6. Freire-Palacios V, Jaramillo-Galarza K, Quito-Calle J, Orozco-Cantos L. La inteligencia artificial en la gamificación para promover la salud mental de los estudiantes universitarios: una revisión de alcance. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología 2023;3:639-639. https://doi.org/10.56294/saludcyt2023639.
7. Ahmed K, Chalmers K, Khlif H. A Meta-analysis of IFRS adoption effects. Int J Account. 2013;48(2):173-217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intacc.2013.04.002
8. Albitar K, Gerged AM, Kikhia H, Hussainey K. Auditing in times of social distancing: the effect of COVID-19 on auditing quality. Int J Account Inf Manage. 2021;29(1):169-178. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJAIM-08-2020-0128
9. Cánovas LPL, Cánovas LBL, Rodríguez YP, Hernández BG, Martín MMP, Montano AL. Evaluation of Burnout Syndrome and associated factors in primary care health personnel. Community and Interculturality in Dialogue 2023;3:73-73. https://doi.org/10.56294/cid202373.
10. Castillo-Gonzalez W, Lepez CO, Bonardi MC. Augmented reality and environmental education: strategy for greater awareness. Gamification and Augmented Reality 2023;1:10-10. https://doi.org/10.56294/gr202310.
11. Aldhyani THH, Alzahrani A. Framework for Predicting and Modeling Stock Market Prices Based on Deep Learning Algorithms. Electronics. 2022;11(19):2-19. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193149
12. Almeida F, Duarte Santos J, Monteiro JA. The Challenges and Opportunities in the Digitalization of Companies in a Post-COVID-19 World. IEEE Eng Manage Rev. 2020;48(3):97-103. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMR.2020.3013206
13. Lepez CO. Invisible challenges in healthcare leadership. Health Leadership and Quality of Life 2023;2:35-35. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl202335.
14. Parra AL, Escalona E, Gollo O. Estudio piloto comparativo de medidas antropométricas en bipedestación entre Tablas antropométricas y un Antropómetro Harpenden. Interdisciplinary Rehabilitation / Rehabilitacion Interdisciplinaria 2023;3:48-48. https://doi.org/10.56294/ri202348.
15. Alqahtani MM. Artificial intelligence and entrepreneurship education: A paradigm in Qatari higher education institutions after COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Data Netw Sci. 2023;7(2):695-706. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2023.3.002
16. AlQershi N, Mohds SS, Abas Z. The relationship between strategic innovations, human capital and performance: An empirical investigation. Sustain Futures. 2021;3(3):100056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sftr.2021.100056
17. Vanoy RJA. Transformación Educativa: Optimización en la Enseñanza de Logística en los Negocios Internacionales mediante la Aplicación de Inteligencia Artificial en Instituciones de Educación Superior. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias 2023;2:422-422. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2023422.
18. Bory E de JP, Naranjo OV, Herrero LB, Flores LGA, Fuentes MGB. Enseñanza híbrida: una innovación docente departamental partícipe de la transformación digital universitaria. Seminars in Medical Writing and Education 2023;2:28-28. https://doi.org/10.56294/mw202328.
19. AlQershi N, Ahmad RB, Bin Abu MF, Permarupan PY, Nik N, Yusoff MNH Bin, et al. The threat of robots to career sustainability, and the pivotal role of knowledge management and human capital. J Innov Knowl. 2023;8(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2023.100386
20. Arrighetti A, Landini F, Lasagni A. Intangible Asset Dynamics and Firm Behaviour. Ind Innov. 2015;22(5):402-422. https://doi.org/10.1080/13662716.2015.1064256
21. Bory E de JP, Naranjo OV, Herrero LB, Flores LGA, Fuentes MGB. Pertinence of the teaching use of virtual classroom by Basic Biomedical Science Department. Seminars in Medical Writing and Education 2023;2:31-31. https://doi.org/10.56294/mw202331.
22. Llana AJO, Ruiz JAZ, Claudio BAM. Quality of service and citizen satisfaction in a Lima district municipality. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:17-17. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa202317.
23. Artemenko DA, Zenchenko SV. Digital technologies in the financial sector: Evolution and major development trends in Russia and Abroad. Finance: Theory and Practice. 2021;25(3):90-101. https://doi.org/10.26794/2587-5671-2021-25-3-90-101
24. Ron M, Pérez A, Hernández-Runque E. Nivel de riesgo para la salud y predicción del dolor musculo-esqueletico en trabajadores en condiciones de teletrabajo: Un enfoque matricial. Interdisciplinary Rehabilitation / Rehabilitacion Interdisciplinaria 2023;3:40-40. https://doi.org/10.56294/ri202340.
25. Castillo-González W. The importance of human supervision in the use of ChatGPT as a support tool in scientific writing. Metaverse Basic and Applied Research 2023;2:29-29. https://doi.org/10.56294/mr202329.
26. Aydin E, Rahman M, Ozeren E. Does Industry 5.0 Reproduce Gender (In)equalities at Organisations? Understanding the Interaction of Human Resources and Software Development Teams in Supplying Human Capitals. Inf Syst Front. 2023. doi:10.1007/s10796-023-10450-1
27. Beames A, Broekx S, Schneidewind U, et al. Amenity proximity analysis for sustainable brownfield redevelopment planning. Landsc Urban Plan. 2018;171(2017):68-79. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.12.003
28. Florentin GNB. The human dimension in nursing. An approach according to Watson’s Theory. Community and Interculturality in Dialogue 2023;3:68-68. https://doi.org/10.56294/cid202368.
29. Barrios CJC, Hereñú MP, Francisco SM. Augmented reality for surgical skills training, update on the topic. Gamification and Augmented Reality 2023;1:8-8. https://doi.org/10.56294/gr20238.
30. Benedikt A, Mirbabaie M, Lembcke TB, Hofeditz L. Ethical management of artificial intelligence. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2021;13(4):1-18. doi:10.3390/su13041974
31. Berhil S, Benlahmar H, Labani N. A review paper on artificial intelligence at the service of human resources management. Indones J Electr Eng Comput Sci. 2019;18(1):32-40. doi:10.11591/ijeecs.v18.i1.pp32-40
32. Ganán K, Chasillacta F. La comunicación en el cuidado humanizado brindado por el profesional de enfermería. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología 2023;3:505-505. https://doi.org/10.56294/saludcyt2023505.
33. Pérez BNP, Miranda GLH, Horta GAH, Vitón-Castillo AA. Tendencias del proceso de gestión del trabajo metodológico en la carrera de medicina. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias 2023;2:487-487. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2023487.
34. Chalmers D, MacKenzie NG, Carter S. Artificial Intelligence and Entrepreneurship: Implications for Venture Creation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Entrep Theory Pract. 2021;45(5):1028-1053. doi:10.1177/1042258720934581
35. Cortado FJ, Chalmeta R. Use of social networks as a CSR communication tool. Cogent Bus Manag. 2016;3(1):1-18. doi:10.1080/23311975.2016.1187783
36. Gonzalez-Argote D, Gonzalez-Argote J. Generation of graphs from scientific journal metadata with the OAI-PMH system. Seminars in Medical Writing and Education 2023;2:43-43. https://doi.org/10.56294/mw202343.
37. Jeronimo CJC, Basilio AYP, Claudio BAM, Ruiz JAZ. Human talent management and the work performance of employees in a textile company in Comas. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:5-5. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa20235.
38. Dini M, Stumpo G. Mipymes en América Latina: un frágil desempeño y nuevos desafíos para las políticas de fomento, Documentos de Proyectos (LC/TS.2018/75). https://repositorio.cepal.org/handle/11362/44148
39. Fuentes DD, Fajardo MA, Diaz JL, Fajardo JE. Impacto social y económico del capital humano en las microempresas : un contraste colombiano y global. Rev Perspect Empresarial. 2021;8(2):104-121. https://revistas.ceipa.edu.co/index.php/perspectiva_empresarial/article/view/721
40. Morgner MI, Djament L. Impact of Preventive and Mandatory Social Isolation in the control of type I diabetes in adults in the Buenos Aires Metropolitan Area. Community and Interculturality in Dialogue 2023;3:82-82. https://doi.org/10.56294/cid202382.
41. Gavilan NE, Paquiyauri YY, Meneses-Claudio B, Lopez-Curasma A, Romero-Sandoval J. Pedagogical Management and Managerial Leadership in the Secondary Educational Institutions of Network 6, UGEL 06, Ate, 2020. Data and Metadata 2023;2:172-172. https://doi.org/10.56294/dm2023172.
42. Fuentes-Doria DD, Toscano-Hernández AE, Malvaceda-Espinoza E, Díaz Ballesteros JL, Díaz Pertuz L. Metodología de la investigación: Conceptos, herramientas y ejercicios prácticos en las ciencias administrativas y contables. In Metodología de la investigación: Conceptos, herramientas y ejercicios prácticos en las ciencias administrativas y contables. https://repository.upb.edu.co/handle/20.500.11912/6201/restricted-resource?bitstreamId=0e63117a-e562-440b-91b8-7081c0736ab5
43. Fuentes JF, Sanz FJ. A custom sensor network for autonomous water quality assessment in fish farms. Electronics (Switzerland). 2021;10(18). doi:10.3390/electronics10182192
44. Montano-Silva RM, Fernández-Breffe T, Abraham-Millán Y, Céspedes-Proenza I, Pantoja-García E. «Tooth fairy» educational strategy for infants in the fifth year of life. Community and Interculturality in Dialogue 2023;3:77-77. https://doi.org/10.56294/cid202377.
45. Ñañez-Silva M, Meneses-Claudio B. University academic tutoring in times of COVID-19. Proposal of strategies from the perspective of the tutor and tutored. Data and Metadata 2023;2:165-165. https://doi.org/10.56294/dm2023165.
46. Garzon MA. Análisis de sostenibilidad, rentabilidad y endeudamiento de SkyNey de Colombia S.A.S a través de indicadores financieros. Universidad Católica de Colombia. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
47. Gómez J, Martínez JA, Lázaro C, García JC. Open innovation during web surfing: Topics of interest and rejection by Latin American college students. J Open Innov Technol Mark Complex. 2021;7(1):1-17. doi:10.3390/joitmc7010017
48. Rasheed Z, Ghwanmeh S, Abualkishik AZ. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Personalized Learning: A Systematic Review. Data and Metadata 2023;2:146-146. https://doi.org/10.56294/dm2023146.
49. Aveiro-Róbalo TR, Pérez-Del-Vallín V. Gamification for well-being: applications for health and fitness. Gamification and Augmented Reality 2023;1:16-16. https://doi.org/10.56294/gr202316.
50. Guha A. Prediction of bankruptcy using big data analytic based on fuzzy C-means algorithm. IAES Int J Artif Intell. 2019;8(2):168-174. doi:10.11591/ijai.v8.i2.pp168-174
51. Hutchins MG, Fletcher D, Hagen-Zanker A, et al. Why scale is vital to plan optimal Nature-Based Solutions for resilient cities. Environ Res Lett. 2021;16(4). doi:10.1088/1748-9326/abd9f4
52. Lobato KJT, Pita DLR, Ruiz GEZ, Claudio BAM. The impact of job performance and performance on workers in northern Lima. Health Leadership and Quality of Life 2023;2:30-30. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl202330.
53. Horta GAH, García ZG. Resultados del tratamiento de rehabilitación física en niños con retardo en el desarrollo psicomotor. Interdisciplinary Rehabilitation / Rehabilitacion Interdisciplinaria 2023;3:28-28. https://doi.org/10.56294/ri202328.
54. Innocenti S, Golin M. Human capital investment and perceived automation risks: Evidence from 16 countries. J Econ Behav Organ. 2022;195:27-41. doi:10.1016/j.jebo.2021.12.027
55. Jaiswal A, Arun CJ, Varma A. Rebooting employees: upskilling for artificial intelligence in multinational corporations. Int J Hum Resour Manage. 2022;33(6):1179-1208. doi:10.1080/09585192.2021.1891114
56. López-Belmonte J, Pozo-Sánchez S, Moreno-Guerrero A-J, Marín-Marín J-A. We’ve reached the GOAL. Teaching Methodology for Transforming Learning in the METAVERSE. A teaching innovation project. Metaverse Basic and Applied Research 2023;2:30-30. https://doi.org/10.56294/mr202330.
57. Moreno AMA, Paredes BAO, Guardias HPT, Palmera BV. Análisis estratégico para la empresa Imbocar, seccional Valledupar – Colombia. Región Científica 2023;2:202395-202395. https://doi.org/10.58763/rc202395.
58. Kc D. Worker Productivity in Operation Management 1300 Clifton Road. December, 1–96. https://www.nowpublishers.com/article/Details/TOM-095
59. Kholod S, Pavlova V, Spitsyna A, et al. Transformation of the personnel management system in the conditions of digitalization of hr processes. Estud Econ Aplicada. 2021;39(6):1-10. doi:10.25115/eea.v39i6.5015
60. Haro AMZ, Mora ÁSR. Malnutrition prevention strategy based on neonatal screening through the metcoff clinical method. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología 2023;3:555-555. https://doi.org/10.56294/saludcyt2023555.
61. Karthikeyan J, Vasanthan R, Dzuvichu K. A sociolinguistic discourse analysis of assimilated English words: a usagebased model of language acquisition. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias 2023;2:600-600. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2023600.
62. Kim HK, Lee CW. Relationships among healthcare digitalization, social capital, and supply chain performance in the healthcare manufacturing industry. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4):1-13. doi:10.3390/ijerph18041417
63. Kuteyi D, Winkler H. Logistics Challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa and Opportunities for Digitalization. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2022;14(4). doi:10.3390/su14042399
64. Lichtensztejn M, Benavides M, Galdona C, Canova-Barrios CJ. Knowledge of students of the Faculty of Health Sciences about Music Therapy. Seminars in Medical Writing and Education 2023;2:35-35. https://doi.org/10.56294/mw202335.
65. Dionicio RJA, Serna YPO, Claudio BAM, Ruiz JAZ. Sales processes of the consultants of a company in the bakery industry. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:2-2. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa20232.
66. Kuzior A. Technological Unemployment in the Perspective of Industry 4.0 Development. Virtual Economics. 2022;5(1):7-23. doi:10.34021/VE.2022.05.01(1)
67. Lassoued R, Macall DM, Smyth SJ, Phillips PWB, Hesseln H. Expert insights on the impacts of, and potential for, agricultural big data. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2021;13(5):1-18. doi:10.3390/su13052521
68. Sánchez RM. Transformando la educación online: el impacto de la gamificación en la formación del profesorado en un entorno universitario. Metaverse Basic and Applied Research 2023;2:47-47. https://doi.org/10.56294/mr202347.
69. Fernández LD, Parrado RP, Cisneros JDD. La gestión del componente laboral a través del acompañamiento a estudiantes en formación. Región Científica 2023;2:202383-202383. https://doi.org/10.58763/rc202383.
70. Li S, Xu C. Research on the Impact of Industrial Robots on China’s Regional Industrial Structure. J Autonomous Intelligence. 2022;5(1):1-12. doi:10.32629/jai.v5i1.498
71. Liu J, Ren L, Chu X, Gong D. The effects of robots on the long-run economic growth. Tehnicki Vjesnik. 2020;27(1):73-80. doi:10.17559/TV-20191010033915
72. Pérez-Hernández G, Téllez NR, C JJR, S LGL, L OG. Use of videos as a method of learning in social service projects. Community and Interculturality in Dialogue 2023;3:100-100. https://doi.org/10.56294/cid2023100.
73. Ezzaim A, Dahbi A, Haidine A, Aqqal A. Enhancing Academic Outcomes through an Adaptive Learning Framework Utilizing a Novel Machine Learning-Based Performance Prediction Method. Data and Metadata 2023;2:164-164. https://doi.org/10.56294/dm2023164.
74. Liu S, Li G, Xia H. Analysis of Talent Management in the Artificial Intelligence Era. Proceedings of the 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Economic Research and Management Innovation (ERMI 2021). 2021;167(Ermi):38-42. doi:10.2991/aebmr.k.210218.007
75. Matute-Pinos K, Bojorque-Chasi R. Support to the human talent subsystems, selection and recruitment from an expert system. Case study. Ingenius. 2021;2021(26):41-48. doi:10.17163/ings.n26.2021.04
76. Romero-Carazas R. Prompt lawyer: a challenge in the face of the integration of artificial intelligence and law. Gamification and Augmented Reality 2023;1:7-7. https://doi.org/10.56294/gr20237.
77. Cantaro JCC, Tello JDLCH, Ruiz GEZ, Claudio BAM. Leadership styles and organizational climate among employees in Lima, Peru. Health Leadership and Quality of Life 2023;2:36-36. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl202336.
78. Mirza N, Hasnaoui JA, Naqvi B, Rizvi SKA. The impact of human capital efficiency on Latin American mutual funds during Covid-19 outbreak. Swiss J Econ Stat. 2020;156(1). doi:10.1186/s41937-020-00066-6
79. Orosoo M, Raash N, Santosh K, et al. Exploring the Influence of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Managing Human Resource Management. J Theor Appl Inf Technol. 2023;101(23):7847-7855. http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol101No23/28Vol101No23.pdf
80. Vallejo RG. Metaverso, sociedad y educación. Metaverse Basic and Applied Research 2023;2:49-49. https://doi.org/10.56294/mr202349.
81. Centon JMG, Cubas WC, Huillcacuri JB, Maldonado ABS. El crecimiento empresarial y su relación en la rentabilidad de una MYPE del rubro comercial en Arequipa, Perú. Región Científica 2023;2:202387-202387. https://doi.org/10.58763/rc202387.
82. Pacheco C, Rojas C, Niebles L, et al. GESTIÓN HUMANA Y SU ESTADO ACTUAL EN LAS PYMES DE MONTERIA. Ediciones Corporación Universitaria Latinoamericana. 2018;1(1):39-63. https://libros.ul.edu.co/index.php/libros/catalog/download/47/19/180?inline=1
83. Sarkar S, Pansera M. Sustainability-driven innovation at the bottom: Insights from grassroots ecopreneurs. Technol Forecast Soc Change. 2017;114:327-338. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2016.08.029
84. Velasco ASD, Ccama FLM, Claudio BAM, Ruiz GEZ. Transformational Leadership as a Driver of Business Success: A Case Study in Caquetá. Health Leadership and Quality of Life 2023;2:37-37. https://doi.org/10.56294/hl202337.
85. Carestia DR, Beltran AF, Cerdera F, Sanchez ML, Ibáñez F. Impacto fisiológico de la respiración, en la salud y en el nivel del estrés. Interdisciplinary Rehabilitation / Rehabilitacion Interdisciplinaria 2023;3:46-46. https://doi.org/10.56294/ri202346.
86. Sima V, Georgiana I, Subic J, Nancu D. Influences of the Industry 4.0. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2020;13(8):4041-4056. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/10/4035
87. Su CH, Cheng TW. A sustainability innovation experiential learning model for virtual reality chemistry laboratory: An empirical study with PLS-SEM and IPMA. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2019;11(4). doi:10.3390/su11041027
88. Yauri-Paquiyauri Y, Enriquez-Gavilan N, Meneses-Claudio B, Lopez-Curasma A, Romero-Sandoval J. Aggressiveness and school coexistence in students of the 6th grade of the educational institution Nº 20595 «José Gabriel Condorcanqui», San Mateo 2021. Data and Metadata 2023;2:169-169. https://doi.org/10.56294/dm2023169.
89. Auza-Santiváñez JC, Díaz JAC, Cruz OAV, Robles-Nina SM, Escalante CS, Huanca BA. Bibliometric Analysis of the Worldwide Scholarly Output on Artificial Intelligence in Scopus. Gamification and Augmented Reality 2023;1:11-11. https://doi.org/10.56294/gr202311.
90. Sun Y. Optimization Stock Portfolio With Mean-Variance and Linear Programming: Case In Indonesia Stock Market. Binus Bus Rev. 2010;1(1):15. doi:10.21512/bbr.v1i1.1018
91. Van Hemert P, Nijkamp P. Knowledge investments, business R&D and innovativeness of countries: A qualitative meta-analytic comparison. Technol Forecast Soc Change. 2010;77(3):369-384. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2009.08.007
92. Torres A, Pérez-Galavís A, Ron M, Mendoza N. Factores Psicosociales Laborales y Estrés en el Personal Médico Asistencial. Interdisciplinary Rehabilitation / Rehabilitacion Interdisciplinaria 2023;3:42-42. https://doi.org/10.56294/ri202342.
93. Cano CAG, Castillo VS, Rojas EEM. Strategy for improving learning in the Financial Tools and Project Management Course through the use of Second Life-SL. Metaverse Basic and Applied Research 2023;2:31-31. https://doi.org/10.56294/mr202331.
94. Votto AM, Valecha R, Najafirad P, Rao HR. Artificial Intelligence in Tactical Human Resource Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Int J Inf Manage Data Insights. 2021;1(2):100047. doi:10.1016/j.jjimei.2021.100047
95. Vrontis D, Christofi M, Pereira V, et al. Artificial intelligence, robotics, advanced technologies and human resource management: a systematic review. Int J Hum Resour Manage. 2022;33(6):1237-1266. doi:10.1080/09585192.2020.1871398
96. Torres MER, Espriella PGDL. Creación de un modelo tecno-pedagógico para el fortalecimiento de la lengua Emberá Katío mediante las costumbres ancestrales en la institución educativa el Rosario de Tierralta. Región Científica 2023;2:202398-202398. https://doi.org/10.58763/rc202398.
97. Estrella NLC, Pérez GPL. Atención de enfermería en pacientes oncológicos con cuidados paliativos. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología 2023;3:488-488. https://doi.org/10.56294/saludcyt2023488.
98. Wang Y, Li C, Khan MA, Li N, Yuan R. Firm information disclosure environment and R&D investment: Evidence from Internet penetration. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(3 March):1-20. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247549
99. Wünderlich NV, Hogreve J, Chowdhury IN, et al. Overcoming vulnerability: Channel design strategies to alleviate vulnerability perceptions in customer journeys. J Bus Res. 2020;116(July):377-386. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.027
100. Salvador VKA, Barrera MJ, Olvera JLC, Chavez MTC, Riva MEM-L. Formación del docente de enfermería en el uso de Innovación educativa en la Atención Primaria Salud: Revisión literaria. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología 2023;3:471-471. https://doi.org/10.56294/saludcyt2023471.
101. Asencios-Trujillo L, Asencios-Trujillo L, Rosa-Longobardi CL, Gallegos-Espinoza D, Piñas-Rivera L. Inteligencia emocional en estudiantes del último año de un programa de educación de una universidad privada en Lima. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias 2023;2:406-406. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2023406.
102. Yang C, Yu M, Li Y, et al. Big Earth data analytics: a survey. Big Earth Data. 2019;3(2):83-107. doi:10.1080/20964471.2019.1611175
103. Zemtsov S, Barinova V, Semenova R. The risks of digitalization and the adaptation of regional labor markets in Russia. Foresight STI Governance. 2019;13(2):84-96. doi:10.17323/2500-2597.2019.2.84.96
104. Rodríguez-Martínez C, Alvarez-Solano J, Pérez-Galavís AD, Ron M. Distance education during the COVID-19 pandemic: experience at a public university. Seminars in Medical Writing and Education 2023;2:32-32. https://doi.org/10.56294/mw202332.
105. David BGM, Ruiz ZRZ, Claudio BAM. Transportation management and distribution of goods in a transportation company in the department of Ancash. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:4-4. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa20234.
FINANCING
The authors received no funding for the development of this research.
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Julio Cesar Gama Espinosa, Lina María Leiva Sánchez, Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira.
Formal analysis: Julio Cesar Gama Espinosa.
Research: Julio Cesar Gama Espinosa, Lina María Leiva Sánchez, Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira.
Methodology: Lina María Leiva Sánchez, Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira.
Resources: Julio Cesar Gama Espinosa, Lina María Leiva Sánchez, Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira.
Software: Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira.
Visualization: Julio Cesar Gama Espinosa, Lina María Leiva Sánchez, Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira.
Writing - original draft: Melisa Andrea Fajardo Pereira.
Writing - revision and editing: Julio Cesar Gama Espinosa, Lina María Leiva Sánchez.