doi: 10.62486/agmu202342
ORIGINAL
Nursing care in post-surgical patient of adnexal cystectomy in the Obstetrics and Gynecology Service of a national hospital of Chincha, 2023
Cuidados de enfermería en paciente posquirúrgica de quistectomia anexial en el Servicio de Gineco Obstetricia de un hospital nacional de Chincha, 2023
Vilma L.
Chumpitaz-Saravia1, Blanca Villaverde-Saravia1, Sofía D.
Vivanco-Hilario1, Wilter C. Morales-García1 ![]() *
*
1Unidad de Posgrado de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Peruana Unión, Escuela de Posgrado. Lima, Perú.
Cite as: Chumpitaz-Saravia VL, Villaverde-Saravia B, Vivanco-Hilario SD, Morales-García WC. Nursing care in post-surgical patient of adnexal cystectomy in the Obstetrics and Gynecology Service of a national hospital of Chincha, 2023. Multidisciplinar (Montevideo). 2023; 1:42. https://doi.org/10.62486/agmu202342
Submitted: 11-06-2023 Revised: 15-09-2023 Accepted: 19-11-2023 Published: 20-11-2023
Editor: Telmo
Raúl Aveiro-Róbalo ![]()
ABSTRACT
The ovarian cyst is a sac with a collection of fluid that forms in the ovary or the wall of adjacent organs. The objective was to manage the nursing care process (PAE) for a post-surgical patient of adnexal cystectomy with right salpingo-oopherectomy with release of adhesions. The study has a qualitative approach, a single case type, the methodology was the PAE, which included a 22-year-old patient, in which the five stages were applied: in the assessment stage, the guide with the 11 functional patterns was applied by Maryori Gordon, 6 altered patterns were found, three being prioritized: cognitive perceptual, exercise activity and metabolic nutritional; In the diagnosis stage, it was developed based on taxonomy II of NANDA-I, 10 nursing diagnoses were identified, prioritizing three: Acute pain, Risk of surgical wound infection and Obesity, according to the SSPFR format (signs and symptoms, problem, related factor/risk factor/associated); In the planning stage, the care plan was developed based on the NOC, NIC Taxonomy; In the execution stage, specific care was provided according to the plan; and in the evaluation the differe nce between the final and baseline scores respectively was assessed, resulting in a score of +2, +1 and +1. In conclusion, the nursing care process for the patient was managed, which allowed quality and holistic care to be provided.
Keywords: Nursing Care; Patient and Adnexal Cyst.
RESUMEN
El quiste ovárico es un saco con colección de líquido que se forman en el ovario o la pared de órganos adyacentes. El objetivo fue gestionar el proceso de atención de enfermería (PAE) a una paciente posquirúrgica de quistectomia anexial con salpingo-oferectomia derecha con liberación de adherencias. El estudio tiene enfoque cualitativo, tipo caso único, la metodología fue el PAE, que incluyo a un paciente de 22 años de edad, en el que se aplicó las cinco etapas: en la etapa de valoración se aplicó la guía con los 11 patrones funcionales de Maryori Gordon, se hallaron 6 patrones alterados, priorizándose tres: perceptivo cognitivo, actividad ejercicio y nutricional metabólico; en la etapa de diagnóstico se elaboró en base a la taxonomía II de NANDA-I, se identificaron 10 diagnósticos de enfermería, priorizándose tres: Dolor agudo, Riesgo de infección de herida quirúrgica y Obesidad, de acuerdo al formato SSPFR (signos y síntomas, problema, factor relacionado/factor de riesgo/asociado); en la etapa de planificación se elaboró el plan de cuidados en base a la Taxonomía NOC, NIC; en la etapa de ejecución se procedió a brindar los cuidados específicos de acuerdo al plan; y en la evaluación se valoró la diferencia entre las puntuaciones final y basal respectivamente, obteniendo como resultado una puntuación de +2, +1 y +1. En conclusión, se gestionó el proceso de atención de enfermería en la paciente, lo que permitió brindar un cuidado de calidad y holístico.
Palabras clave: Cuidados de Enfermería; Paciente y Quiste Anexial.
INTRODUCTION
The incidence of adnexal cysts worldwide is 6,21 % in women younger than 20 years; the prevalence is estimated at 4,9 per 100 000 women.(Gonzalez-Menocal et al., 2019). Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine-metabolic abnormality, with a worldwide prevalence equivalent to 4 % to 21 %, according to diagnostic criteria.(Ordinola et al., 2022). It is estimated that 10 % of women will have an adnexal pathology in their lifetime; the highest percentage of lesions that are operated on are benign (Rodriguez et al., 2017).
Internationally, in the USA, the estimate of women undergoing surgery for adnexal masses is more than 200 000 women per year (De Matías et al., 2020). In Bolivia, they found cases in clinical stage III of the disease, where the main symptom was abdominal pain and increased abdominal perimeter; the histopathological type of adnexal masses were epithelial tumors with 43,75 % and germinal tumors in 17,85 % of cases (González, 2022).
According to Cano (2022), MINSA considers that there are associated risk factors such as obesity in more than 50 %, type II diabetes, glucose intolerance, metabolic syndrome, and dyslipidemia, with many alterations such as ovulatory dysfunction due to altered folliculogenesis and hyperandrogenism. In Lima, it is the most common disease in women of childbearing age (15 to 49 years), and 70 % of those who suffer from it have not been diagnosed. It is also said that this pathology affects 8 % to 13 % of the female population. At the Hospital
Virgen de Fátima, Chachapoyas, studied 300 medical records from 2018, finding a prevalence rate of PCOS of 52,6 per 100 patient records attended. Ultrasonography was a conclusive diagnostic tool for medical diagnosis (Ordinola et al., 2022).
Adnexal cysts are fluid collections in the pelvic area around the uterus, encompassing the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and other adjacent tissues. Simple ovarian cysts often form during the normal menstrual cycle and are not listed as a problem (Defaz, 2017).
The etiology is unknown, but studies show an association with increased concentrations of chorionic gonadotropin or abnormal ovarian response to this hormone. It is frequently asymptomatic and discovered accidentally, usually in acute abdominal pain or abdomen due to ovarian torsion or hemorrhage. On some occasions, it can be confused with malignant ovarian neoplasms (Reyna-Villasmil et al., 2020).
As for the pathophysiology, month, during the menstrual cycle, a follicle develops in the ovary; if this follicle does not rupture and release an egg, the liquid remains inside it, and a cyst is formed; this is called a follicular cyst and when a follicle makes the egg independent, it begins to produce estrogen and progesterone for fertilization. The follicle is now called the corpus luteum. Sometimes, fluid is stored within the follicle, which causes the corpus luteum to enlarge and form a cyst called a corpus luteum cyst (Martinez et al., 2022a).
The clinical picture manifests with intense pain in the hypogastrium (radiating to the flanks or lumbar region), nausea, vomiting, and thermal rise, which occurs rarely. On physical examination, a palpable mass can be perceived. Among the useful ultrasound findings described is the appearance of a cystic mass (solid or complex, with or without pelvic fluid) with wall thickening and hemorrhage. (Ramirez and Rengifo, 2019).
The fundamental point of treatment in ovarian tumors is to diagnose and differentiate between functional cysts (follicular), benign tumors, or malignant tumors. There are two possible approaches: control or surgery. Surgical treatment may include Cystectomy, Oophorectomy, or adnexectomy (Gomez et al., 2022).
The Nursing Care Process, as a scientific method, guides the nurse's work to provide scientific, humanistic, and systematic care. The main activity of the nurse is constant evaluation of the patient's pathophysiological changes and improvement, assessing their welfare from the care provided. The application of PAE quality and timely and safe care is essential to achieving prompt recovery of their health. (Martínez et al., 2022b).
Obstetrics and gynecology nursing care is important because it provides comprehensive care to people, supported by scientific evidence (Miranda-Limachi et al., 2019). This requires comprehensive and technical preparation in knowledge, procedures, and skills, including health education, from a biological, psychological, and social perspective (Borges et al., 2018). In this sense, they are an integral part of the multidisciplinary team, strategic and essential to protect the right to health of the female population.
METHOD
The present study took a qualitative, single-case approach, applying the nursing care process as a tool with a series of closely interrelated stages. To organize nursing work, it is necessary to gather information, formulate the diagnosis, plan the interventions, administer them to achieve the results, and then formulate the evaluation (Herdman et al., 2021).
The subject of the study was a 22-year-old patient diagnosed with a right adnexal cyst after immediate surgery of cystectomy with right salpingo-oophorectomy, release of adhesions, and placement of a drain pen rose and obesity, selected at the convenience of the researchers. For the assessment, we used observation technique, physical examination of the patient, interview, and documented review based on the clinical history; as a basic instrument, we used an assessment guide based on the 11 functional patterns of Maryori Gordon; after the critical analysis of the significant data, nursing diagnoses were formulated taking into account the NANDA-I taxonomy II; for the planning stage, we used the NOC and NIC taxonomy. After the nursing care execution stage, the process culminated with the evaluation, which was given with achievement scores obtained from the difference between the final and the baseline scores.
Nursing Care Process Assessment
General Data
Name: GALC Sex: Female Age: 22 years old
Days of nursing care: 24 hours Date of assessment: 7/10/22
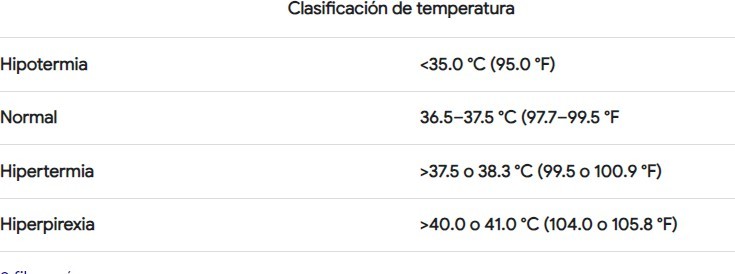
Reason for admission: The patient is referred from the post-anesthesia recovery unit to the gynecology department on a stretcher accompanied by nursing staff, with a medical diagnosis of salpingo-pherectomy right+ release of adhesions+ dren pen rose. On assessment, the patient was lucid, oriented in time, space, and person, and ventilating spontaneously with a peripheral line perfusing fluids. The operative wound in the right flank quadrant of the abdomen, protected with a dry dressing and drain pen, rose with drainage in a colostomy bag, with little content of schematic secretion. Blood pressure control 100/60 mm Hg, pulse 78/minute, respiratory rate 17/minute and temperature 36.5 °C.
Assessment according to Functional Health Patterns
Functional Pattern I: Perception - Health Control. History of diseases, in February 2022 a giant benign cyst was detected in the right ovary, with hormonal treatment for 3 consecutive months and then the patient abandoned the treatment.
Surgical history: Cesarean three years ago, operated on right adnexal cyst by emergency 12 hours ago. She is not allergic to medications or food. Good hygiene status. No risk factors, with four doses of Sarcovid-19 vaccine.
He is currently receiving treatment with clindamycin 600 mg EV c/8 hours, ceftriaxone 2 g EV c/24 hours, metamizole 2 g EV c/8 hour.
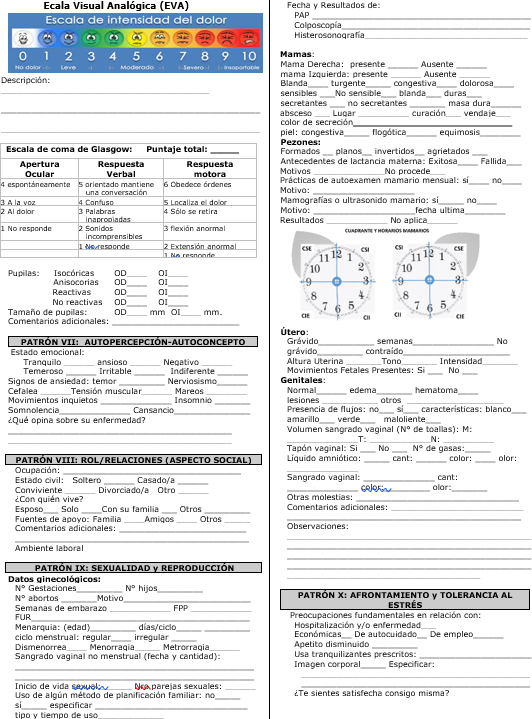
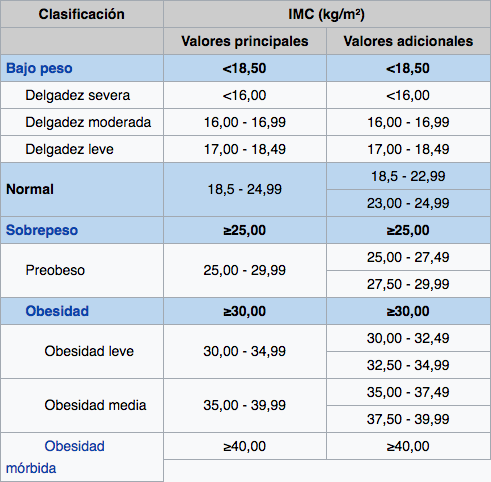
Functional Pattern II: Metabolic Nutrition. Weight 105 kg, height 1,60, obesity III by BMI of 41 kg/m2. Skin, warm, hydrated with mild pallor and normal temperature of 36,6 ° C, normal hair.
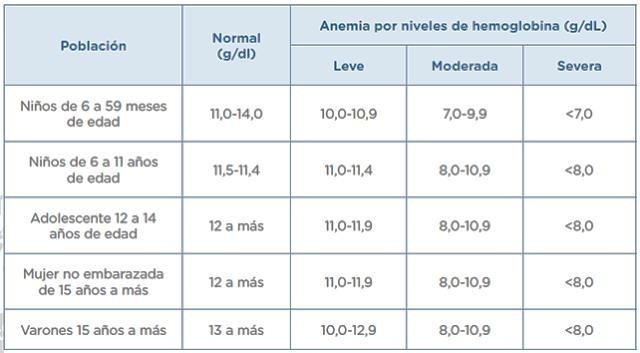
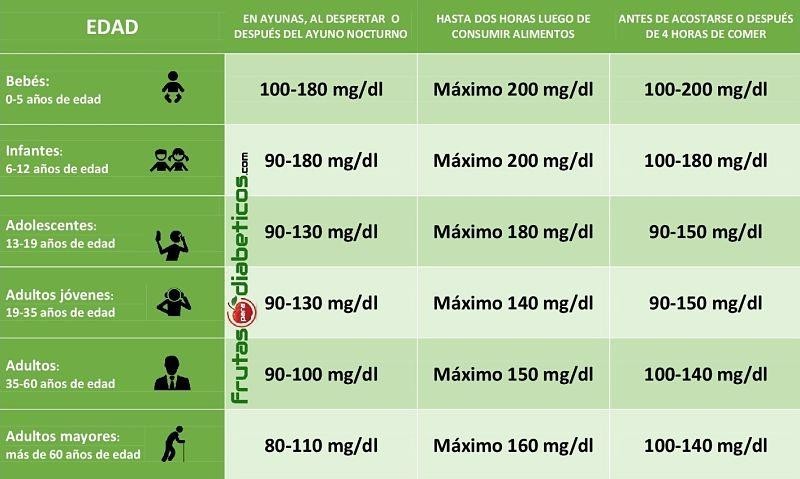
Soft and depressible abdomen, painful in the operative area, operative wound with Pfannenstiel incision, with presence pen rose drain and drainage to a colostomy bag, mild anemia with hemoglobin 10,7 mg/dl, normal basal glucose analysis of 110 mg/dl, has lost 3 kg of weight compared to the date of admission, tolerates soft diet and oral fluids according to medical indications. Diet with consumption of sugary drinks and fried foods.
Functional pattern III: Elimination. Patient did not have a bowel movement since the previous day, eliminates flatus normally, uses diaper for vaginal bleeding in small amount, colostomy bag hematic fluid content 20 ml. and dry dressing.
Functional Pattern IV: Activity - Exercise. Respiratory Activity: Normal respiratory rate with 20 breaths x min, no cough or secretions, spontaneously ventilating with normal oxygen saturation of 98 %. Circulatory activity: Presents normal levels of peripheral pulse with 80 x min, systolic blood pressure 110 and diastolic blood pressure 70mhg, normal capillary filling (<2 seconds), presence of invasive line, with peripheral catheter number 18 Gauges and 38 millimeters in left upper limb, there is operative wound in the right flank of the abdomen with the presence of drain pen rose and colostomy bag for collection of secretion, containing 20 ml of serohematic fluid. Exercise Self-care capacity: Dependent, manifests pain in operative wound 6/10 according to VAS scale that limits his mobilization to get out of bed.
Pattern V: Rest - Sleep. Patient reports that she had falling asleep due to the noises, she slept alertly for approximately 5-6 hours.
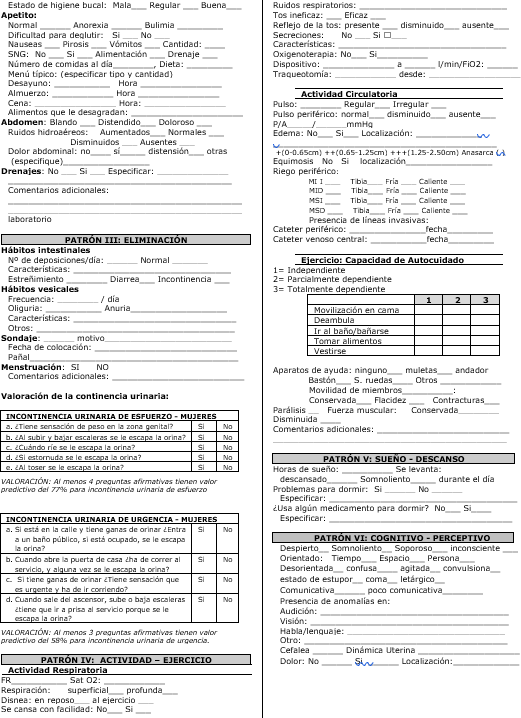
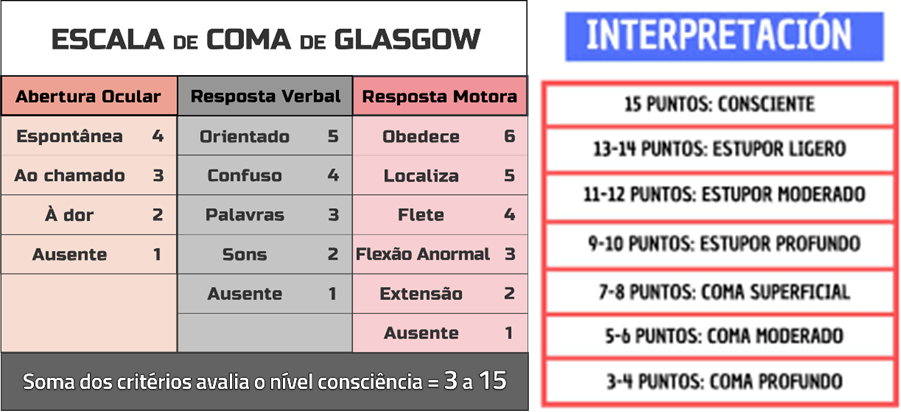
Functional Pattern VI: Perceptive - Cognitive. Level of consciousness, she is awake and oriented in time, space and person, conscious according to Glasgow scale (15 points). Pupils isochoric, manifests pain in the operative area, she is evaluated using the standardized pain instrument Eva scale with a score of 6/10.
Pattern VII: Self-perception - Self-concept Tolerance to stress. Patient receives support from her relatives. She is anxious due to pain in the surgical area, she says that she is very chubby, and this would make her recovery difficult, she also refers that she is a victim of bullying friends and neighbors.
She is concerned about her husband's income, which is not enough to cover the family's expenses because he will stop working until he recovers.
Pattern VIII: Relationships - Role. She has a good relationship with her relatives, who are attentive to her health situation; she lives with her husband and a 3-year-old son.
They have no addiction problems and deny having marital problems.
Pattern IX: Sexuality - Reproduction. Presence of sero-hematic secretions in genitals, with the use of disposable diapers due to the presence of vaginal bleeding in small amounts, she refers that her first menarche was 10 years of age.
Pattern X: Adaptation - Stress Tolerance. Patient is worried about her only who is not used to being without her.
Pattern XI: Values and Beliefs. Religion, she is baptized in the Christian religion. In her religious restriction she does not wear tight-fitting clothes, keeps her hair long, does not dance and does not drink liquor. Practicing Christian religion.
Prioritized Nursing Diagnosis
First Diagnosis
Diagnostic label: (00132) Acute pain.
Defining Characteristics. Facial expression and verbalization of pain, rating of 6/10 on Eva.
Related Factor. Physical injury agent, associated with operative wound.
Diagnostic Statement. Acute pain related to physical injury agent associated with operative wound evidenced by facial expression, verbalization of pain and rating of 6/10 on Eva.
Second diagnosis
Diagnostic Label (00266) Risk of surgical wound infection.
Risk Factors. Obesity.
Associated condition. Invasive procedure in abdominal area, presence of drain pen rose with colostomy bag.
Diagnostic Statement. Risk of surgical wound infection as evidenced by obesity, associated with invasive procedure and drain pen rose to colostomy bag.
Third diagnosis
Diagnostic Label (00232) Obesity.
Defining Characteristics. Morbid obesity with BMI> 41 kg/m2.
Related Factor. Consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages and frequent intake of fried foods and abnormal eating behavior patterns.
Diagnostic Statement. Obesity related to consumption of sugary drinks and intake of fried foods and abnormal eating behavior patterns evidenced by morbid obesity with BMI > 41 kg/m2.
Planning
Care Plan
First Diagnosis (00132) Acute pain.
Nursing Outcomes. NOC: (2102) Pain level.
Indicators
· Referred pain
· Facial expression of pain
· Concern
· Muscle tension
Nursing Interventions. NIC (1410) Acute pain management.
Activities
· Perform an exhaustive pain assessment, including pain localization
· Identify the intensity of the pain
· Ask the patient about the level of pain assessed on the Eva scale.
· Administration of analgesic according to medical prescription.
· Administer non-pharmacological interventions according to the patient's preferences.
Second Diagnosis (00266) Risk of surgical wound infection.
Nursing Outcomes. NOC (1842) Knowledge of infection control.
Indicators
· Signs and symptoms of infection.
· Infection control procedures.
· Importance of hand hygiene.
Nursing Interventions. IAS (6550) Infection protection.
Activities
· Observe for signs and symptoms of systemic and localized infection.
· Observe the patient's vulnerability to infection.
· Administer the indicated antibiotics: clindamycin and ceftriazone, complying with the five correct ones.
· Body temperature monitoring every six hours.
· Maintain asepsis in all procedures.
Third Diagnosis (00232) Obesity.
Diagnostic Label. NOC (1004) Nutritional status.
Indicators
· Nutrient intake.
· Food intake.
· Weight/height ratio.
Nursing interventions. NIC (5246) Nutritional counseling.
Activities
· To assist in the identification of the eating behaviors to be changed.
· Establish executable short-, medium- and long-term goals for change in nutritional status.
· Facilitating care by a nutrition professional for information about the need for dietary modification for health reasons (weight loss)
· Participate with the patient in measuring fluid intake and elimination, blood pressure readings, weight gain and loss every day.
· Provide information about the need for dietary modification based on weight loss, fluid intake and recommended diet.
Execution
|
Table 1. Implementation of the acute pain management intervention for acute pain diagnosis |
||
|
Intervention: Acute pain |
||
|
Date |
Time |
Activities |
|
07/11/2022 |
8:00am 08:05am 08.05am
08.10am 10:00am |
An exhaustive pain assessment is performed, including pain location Pain intensity is identified The patient is asked about the level of pain, assessed on the Eva. Analgesic is administered according to the medical prescription. Non-pharmacological interventions are administered according to the patient's preferences. |
|
Note: prepared from the Nursing Intervention Classification (NIC) (Butcher et al., 2018a). |
||
|
Table 2. Protection against infections for diagnosis Risk of infection in the surgical wound |
||
|
Intervention: protection against infection |
||
|
Date |
Time |
Activities |
|
07/11/ 2022 |
7:30 am 7.40 am 8.20 am 12.00 am. |
Signs and symptoms of systemic and localized infection are observed. The patient's vulnerability to infections is observed. The indicated antibiotics are administered: clindamycin and ceftriaxone, complying with the five correct ones. Body temperature control is monitored every six hours. Asepsis is maintained in all procedures. |
|
Note: prepared from the Nursing Intervention Classification (NIC) (Butcher et al., 2018b). |
||
Table 3. Implementation of the intervention Nutritional status for the diagnosis of obesity |
||
|
Intervention: helps to reduce weight |
||
|
Date |
Time |
Activities |
|
07/11/2022 |
8:00 am 8:20 am 2.00 pm 5.00 pm 3.00pm |
It helped in the identification of the eating behaviors to be changed. Short-, medium- and long-term executable goals were established for the change of nutritional status. Facilitated attention by a nutrition professional for information about the need for dietary modification for health reasons (weight). Fluid intake and elimination measurements, blood pressure readings, weight gain and loss were taken with the patient every day. Information was provided on the need for to modify the diet according to weight loss, fluid intake and recommended diet. |
|
Note: developed from the Nursing Intervention Classification (NIC) (Butcher et al., 2018c). |
||
Evaluation
Result: Pain level
|
Table 4. Baseline and final score of outcome indicators pain level |
||
|
Indicators |
Baseline score |
Final score |
|
Referred pain |
2 |
5 |
|
Facial expression of pain |
2 |
4 |
|
Concern |
2 |
4 |
|
Muscle tensión |
2 |
4 |
|
Note: prepared from the Classification of Outcomes. (NOC) (Moorhead et al., 2018a). |
||
In table 4 fashion of the selected pain level outcome indicators for the diagnosis Acute pain, before the nursing interventions the baseline score was 2 (substantial), after the, the fashion was 4 (mild), corroborated with the patient's verbal expression and improvement with the Eva scale assessment. The change score was +2.
Outcome: Knowledge: infection control
Table 5. Baseline and final score of the knowledge outcome indicators: infection control |
||
|
Indicators |
Baseline score |
Final score |
|
Signs and symptoms of infection Infection Control Procedures Importance of Hand Hygiene |
2 3 3 |
4 4 4 |
|
Note: developed from the No Outcome Classification (NOC) (Moorhead et al., 2018b). |
||
Table 5 shows that the mode of outcome indicators of knowledge of infection control: infectious problem, selected for the diagnosis Risk of infection of the operative wound before the nursing interventions was 3 (moderate knowledge) and after the interventions was 4 (substantial knowledge) with all the care provided, there was evidence of afebrile stage, decrease of secretions through the drain pen rose and better general condition. The change score was +1.
Result: Nutritional Status
|
Table 6. Baseline and final score of outcome indicators Nutritional status |
||
|
Indicators |
Baseline score |
Final score |
|
Nutrient intake |
2 |
3 |
|
Food intake |
3 |
2 |
|
Weight/height ratio |
2 |
3 |
|
Note: developed from the Classification of Outcomes (NOC) (Moorhead et al., 2018). |
||
Table 6 shows that the mode of the adherence behavior outcome indicators: healthy diet, selected for the diagnosis Obesity, before nursing intervention was 2 (Substantial deviation from normal range), after care management was 3 (Moderate deviation from normal range), corroborated with the acceptance of the hypoglycemic, hypocaloric and hyposodium diet with fiber. The change score was +1.
RESULTS
As for the assessment phase, objective and subjective data were collected, the patient was the primary source of information, the clinical history was used, the data was corroborated with the cephalo-caudal physical examination, and then the information was organized with an assessment guide based on the functional health patterns of Maryori Gordon, which was adapted for the obstetrics and gynecology service, in this phase there were no difficulties in conducting the interview.
In the diagnostic phase, the analysis of the significant data according to NANDA-I was carried out, obtaining six altered nursing diagnoses, of which three were prioritized:
(00132) Acute pain, (00266) Risk of infection in the operative wound, and (00132) Obesity; at this stage, developing nursing diagnoses was not difficult.
In the planning phase, considering the NOC and NIC taxonomies, the analysis was carried out to determine nursing outcomes that were best related to the nursing diagnoses, and interventions that were consistent and/or coherent with the outcomes were selected. The difficulty in this phase was in the determination of the scoring of outcome indicators both at baseline and at final evaluation.
During the implementation phase, the care plan prepared for the patient's case was put into practice without major difficulties. New data continued to be evaluated, and at the same time, the care plan was updated and implemented in a comprehensive manner with quality and warmth.
The evaluation phase allowed us to provide feedback on each phase during the care provided to the patient until the patient was discharged without health risks or complications.
DISCUSSION
Acute Pain
Pain is a first line health problem and the physiological response of pain is a product of tissue damage, it is very important to take a complete and detailed clinical history (VAS scale) (León, et al., 2022).
Likewise, Diaz and Flores (2021a) report that pain is a symptom of major consultation in the emergency department. The physiological response of pain is the product of tissue damage generating a chemical response producing an electrical impulse, to finally pain.
Next, we mention what Ardila et al. (2022a) indicate: pain persists in the presence of damage or disease and disappears when the cause or root cause is eliminated. Generally, acute pain is intense, and NSAIDs are first-line drugs for pain management.
The patient presented as a related factor: a physical injury agent associated with an operative wound. Pain persists in the presence of damage or disease and disappears when the cause is eliminated with the administration of drugs (Ardila et al., 2022b).
The patient under study showed defining characteristics: facial expression of pain, facial expression and verbalization of pain, a rating of 6/10 on the Eva scale; Diaz and Flores (2021b) mention that pain is a physiological response as a result of tissue damage, it generates a chemical response producing an electrical impulse, to finally perceive the pain, of which, the nursing plan would be to calm the patient's pain by assessing the level according to the standardized Eva scale instrument.
In relation to the verbalization of pain, Ferran (2021) mentions that there are accurate methods for assessing pain, and various instruments help to assess and measure the pain manifested by the patient.
Measuring pain is an activity of the nursing professional; it requires observation and humanized communication with the patient; in this case, the patient expressed the discomfort of pain. The visual analog scale (VAS) helps to assess the perception of pain considering that it is susceptible and valid to measure pain in people with different levels of reaction to the intensity of pain, it is reproducible among other professionals, and it is easy to use (Delgado, 2020). In this case, the VAS scale was applied, and the patient verbalized a score of 6 on a scale of zero to 10, obtaining a valuation of 6/10 as a result.
About the pain management intervention, the following activities were carried out:
The exhaustive pain assessment, which includes localization, was performed. This task allows the application of many assessment scales and questionnaires to validate the pain through an interview, observation, and exploration. However, all are valid; it will depend on the researcher which one to use according to the case, his experience, and the study objective (Vicente-Herrero et al., 2018).
Pain intensity was also identified. The health professional must use scales that measure pain intensity and indicate whether the treatment was effective or not. The VAS scale is the most appropriate pain intensity assessment. In this case, the patient was reevaluated using the same VAS scale, with a thorough exploration of the history and a rethinking of the nursing care plan to address this symptom (García et al., 2022).
In addition, the patient was asked about the level of pain assessed according to the Eva scale because pain is a subjective phenomenon (symptom) that will affect other dimensions of the organism (sensory, physiological, affective, cognitive, and sociocultural). Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate each dimension and ask the patient how much she measures the level of pain on the EVA scale, considering from no pain (zero points) to extreme pain (10 points), and to determine the patient's perception of pain (Sanz, 2021). The patient reported a score of 6/10 on the VAS scale, considering it as severe pain.
Analgesic treatment was administered with metamizol 2 g EV every 8 hours and tramadol 100 mg conditional to pain greater than seven on the VAS scale. Analgesics are drugs that inhibit cyclooxygenase, block the production of prostaglandins that are responsible for the inflammatory response and pain at peripheral and central levels, helping to alleviate or suppress pain, the
WHO suggests the gradual use of analgesic medication about the patient's response, i.e., the use of a peripheral analgesic (NSAID) or an opioid will depend on the intensity of the pain (Maria-Josep Divins, 2023).
Non-pharmacological interventions, such as postural changes, deep breathing, antalgic position, etc., were also performed according to the patient's preferences, which helped to reduce pain. Ruiz et al. (2021) demonstrated that the non-pharmacological actions contributed to reducing pain as assessed with the VAS scale, decreased analgesic consumption, better attitude to life and the disease, decreased anxiety, improved sleep time, better pain control, and above all, acceptance of pain.
Risk of Infection in the Operative Wound
Surgical site infections are a frequent complication worldwide.
It increases morbimortality in patients with risk factors such as age, gender, chronic pathologies (diabetes mellitus, obesity, immunological diseases, etc.), or wound contamination (Gutiérrez et al., 2023).
Surgical wound infection is manifested by the presence of microorganisms such as staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, or enterococci. It is necessary to treat with broad-spectrum antibiotics. Infection depends on endogenous and exogenous factors, and therefore, antibiotic prophylaxis appropriate to the patient's clinical signs is necessary (Cajamarca et al., 2023).
Rodriguez et. al (2020) studied the risk factors and prevention of infections in the surgical site and concluded that it is important to protocols and practices of asepsis and antisepsis measures and the use of antibiotics to prevent infections. Obesity is a factor three times the risk of causing infection in the operative wound. The patient has obesity III due to a BMI of 41 kg/m2 and is therefore at risk of presenting an infection in the operative wound.
In the nursing intervention of protection against infections, health professionals must comply with good practices of preventive measures to reduce nosocomial infections; they should have knowledge and professional experience associated with this preventive practice (Yagui et al., 2021). The preventive actions implemented by the health professional were to maintain good biosafety practices and to provide personnel with experience in the care of gynecological patients.
The nursing activity is to observe the signs and symptoms of systemic and localized infection. In an infectious operative wound process, it is necessary to intervene early to expect it to develop into a complication and consequent disruption to routine incisional healing post-surgery, including surgical site infection, tissue dehiscence, hyper granulation, peri-injury skin maceration or adhesive skin damage (International Surgical Wound Complications Advisory Panel [ISWCAP], 2020). During the patient's surgical wound assessment, signs and symptoms of no localized or systemic infection were evident, evidenced by typical vital signs and characteristics of the incision site with no changes in its structure.
Observing the patient's vulnerability to infections is an activity that allows the assessment of endogenous and exogenous factors to determine the state of vulnerability to infections. Exogenous factors are external causes that expose the patient to an infectious focus, and endogenous factors or internal causes derive from the pathophysiology, immunity status, and the presence of metabolic or carcinogenic diseases to acquire an infection. Anamnesis and biosafety measures are important if the patient is not infected.
The patient's endogenous conditions are present (MINSA, 2021). Due to obesity III, the patient is considered vulnerable to infections, and biosecurity has been applied.
Antibiotics were administered: clindamycin 600mg every 8 hours and ceftriaxone 2g every 24 hours, meeting the five correct ones. Clindamycin is a macrolide that acts at the level of bacterial protein synthesis for treating severe infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, group A streptococcus (S. pyogenes), skin and soft tissue infections (complicated and uncomplicated). Ceftriaxone is a third-generation cephalosporin used in complicated skin and soft tissue infections and prophylaxis of postoperative infections. The action of both antibiotics is broad-spectrum; they eliminate the action of bacteria, reducing their growth and multiplication (Vera, 2021).
Body temperature monitoring every six hours. It is a preventive and alert activity for detecting sub-febrile states that indicate the increase of organic defense against the invasion of microorganisms. It is a safety measure care in the postoperative period that alerts states of infection in the surgical site, considering that a patient with infection in the operative wound has five times more mortality risk than a non-infected patient (Martinez et al., 2022).
Likewise, asepsis was maintained in all procedures to avoid transmitting germs from one place to another; it is a preventive and promotional measure in health care. Hand washing is a habit that saves lives, especially in patient care, to prevent transmission, spread of infections, and nosocomial infections WHO, 2022).
Obesity
Obesity is considered a chronic non-communicable disease, is associated with other comorbidities, and becomes a negative and relevant factor in the performance of surgical procedures due to postoperative complications (Añez et al., 2021).
Obesity is an abnormal state of the organism caused by excessive accumulation of body fat that is detrimental to health. It is very easily associated with other chronic diseases. Worldwide, more than 3 % of the population is morbidly obese. WHO considers obesity as a body mass index (kg/m) greater than 30 (Nazar et al., 2018).
The patient under study showed the following characteristics: morbid obesity with a BMI> 41 kg/m2. The WHO (2021), in its publication Obesity and Overweight, states that obesity is linked to the intake of high-calorie and high-fat foods and a sedentary lifestyle. The consequences are non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and locomotor system disorders. Obesity in the postoperative period has a high risk of presenting coagulopathies, infections, and renal insufficiency, generating serious complications and more extended hospital stays.
In turn, the consumption of sugary drinks, frequent fried foods, and abnormal eating behavior patterns were considered as related factors. For Zila-Velasque et al. (2022), negative patterns in eating behavior are related to psychiatric alterations in eating and weight control with physical, social, and psychological affection; the person experiences dissatisfaction with the perception of food, body image, fear of weight gain and obsessive thinking about eating. This abnormal eating behavior problem is a public health problem.
Obesity is a risk factor for diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular pathologies, cancer, and psychological conditions. The increase in adiposity in obesity becomes a risk factor for surgical wound infection; the nurse's role is important because he/she must identify complications early (Kaufer-Horwitz et al., 2022). The patient presented a BMI > 41 kg/m2; the probability is high of presenting infection at the incision site; however, personal hygiene measures and healing of the surgical wound twice a day are continued.
The nursing intervention to help reduce weight is necessary to include the patient in a dietary program based on vegetables and physical exercise, which will help control obesity, reduce body fat, reduce anthropometric perimeters, reduce blood pressure values, and above all, reduce the high risks of acquiring chronic diseases (Cari, 2022). The actual conditions of the patient are related to a sedentary lifestyle and uncontrolled food consumption without a dietary regimen and control of chronic diseases.
The activity to determine the patient's desire and motivation to reduce weight or body fat is related to the commitment to solve the problem of obesity, to propose eating habits that promote education on diet quality and exercise to reduce obesity, improve the quality of life and reduce the onset of metabolic diseases at an early (Morocho & Llallahui, 2022). In the case of the patient with obesity III, it will be necessary for her to provide nutritional instruction with a feeding program according to her occupational conditions to reduce her body weight and adipose tissue.
Matching diets to lifestyle and activity levels, including fiber, requires a healthy lifestyle program that includes a design.
They recommend the consumption of fruits and vegetables of all colors in five portions, which provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals; avoid consumption of packaged or processed products; and reduce the consumption of reused fats. They recommend the consumption of fruits and vegetables of all colors in five servings, which provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals; avoid consuming packaged or processed products; and reduce the consumption of reused fats. (Lopez, 2021). The patient's eating problem requires developing a dietary plan according to the accessibility of products and the process of unlearning the consumption of foods harmful to her health.
To encourage the substitution of undesirable habits for favorable habits by giving priority to
proteins, vitamins, and iron, it is necessary to plan healthy food schemes with professional specialists that contain macro and micronutrients to cover physiological needs, so they must be varied, balanced in proportions, and healthy. Bad eating habits such as fasting, standing up, frequent meals, skipping meals, or eating in abundant volume increase body weight. These habits can be improved if we practice the approach of reflecting on eating, replacing unhealthy foods with healthier ones, and reinforcing our new eating habits (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2021). In this case study, the patient has not yet become aware of initiating a dietary plan to replace unhealthy habits with healthy ones.
Placing written indications and encouragement to achieve behaviors that favor health instead of eating is an activity that will allow one to achieve a healthy life; it is a priority to change eating behavior and to know how to face stress and anxiety situations, especially to maintain a good mood because it is the ingredient of life and wellbeing. The behaviors to
Modify requires a list of activities that should be posted in a visible place; it should include meal times and portions, frequency of water consumption, physical exercise, mental exercise, walking, social gatherings, sleeping or resting hours, maintaining a positive attitude and feelings (Basque Government, 2022). To help the patient improve her eating behavior, she will have strict supervision and control the activities to be considered in the calendar, trying to keep her in good spirits to comply with it strictly.
CONCLUSIONS
The human care based on the PAE allows us to provide nursing care from assessment, diagnosis, planning, execution, and evaluation of the planned actions, which allows us to provide comprehensive, continuous, and permanent care during 24 hours, as to rethink the care required by the patient at different times. During the care, an interactive relationship was maintained between the patient and the nursing professional, which allowed us to offer constant monitoring with the possible detection of complications. As a whole, the interdisciplinary work allowed the patient's prompt recovery.
The use of the NANDA, NIC, and NOC relationship allows for analyzing the choice of the nursing diagnosis, then determining the results and the interventions with their respective activities related to the case study, with the purpose of using a unified language based on scientific knowledge.
Finally, the nursing care administered to the patient in her postoperative stage had favorable results for our patient that contributed to an early recovery without complications.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Alcaide-Jiménez, A., Arredondo-Provecho, A. B., Díaz-Martín, M., Alonso-García, M., Rodríguez-Villar, D., Durán-Poveda, M. y Rodríguez-Caravaca, G. (15 de Junio de 2022). Adecuación de la higiene prequirúrgica de manos en un hospital universitario de Madrid. Revista española de Salud Pública, 96, 1-9. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=8620614
2. Amado, E., Garcia, D., & Pulache, A. (2017). Conocimiento y prácticas de cuidado en los padres/tutores de niños colostomizados atendidos en el Hospital San Bartolomé, 2017 [Trabajo académico de licenciatura, Universidad Peruana Unión]. Repositorio institucional. https://repositorio.upeu.edu.pe/handle/20.500.12840/792
3. Añez Ramos, R., Rivas Montenegro, A., González Fernández, L. y Muñoz Moreno, D. (21 de Julio de 2021). Obesidad como factor de riesgo para complicaciones postquirúrgica en la cirugía estética. Revista Latinoamericana de Hipertensión, 16(5). https://www.revhipertension.com/rlh_5_2021/10_obesidad_como_factor_riesgo.pdf
4. Ardila, A., Vargas, J. y De la Espriella, M. (2022). Estrategias alternativas para el manejo del dolor crónico en adultos [Trabajo académico de grado, Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia]. Repositorio institucional. https://repository.ucc.edu.co/entities/publication/3d610e2d-1ebf-493d-8a47- 22d0f1af3da3
5. Arias Huapaya, M. V. (2022). Plan de intervención en el control y monitoreo de las infecciones asociadas a sitio quirúrgico en el hospital Aurelio Díaz Ufano y Peral – Lima, 2022 [Trabajo académico de licenciatura, Uiversidad nacional del Callao]. Repositorio institucional. https://repositorio.unac.edu.pe/handle/20.500.12952/6899
6. Butcher, H., Bulechek, G., Dochterman, J. y Wagner, C. (2018). Clasificación de Intervenciones de Enfermería (NIC). ELSELVIER.
7. Cano, A. (2022). EsSalud advierte que el 70% de mujeres con ovario poliquístico no ha sido diagnosticado. El peruano. Recuperado de: https://elperuano.pe/noticia/190684-essalud-advierte-que-el-70-de-mujeres-con-ovario-poliquistico-no-ha-sido-diagnosticado
8. Cari Huanca, G. (Marzo de 2022). Programa de intervención: Dieta integral y ejercicio físico en la reducción de parámetros antropométricos en Salvador de Bahia-Brasil. Revista de la Facultad de Medicina Humana, 22(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.25176/RFMH.v22i1.4338
9. Carmona, F. (2019). Tumor benigno de ovario. Women's. Recuperado de: https://www.drfcarmona.com/tumor-benigno-de-ovario/
10. Carvajal, C. (2017). Sindrome metabólico definiciones, epidemiología, etiología, componentes y tratamiento. Medicina Legal de Costa Rica, 34(1). https://www.scielo.sa.cr/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1409-00152017000100175
11. CDC (16 de diciembre de 2021). Cómo Mejorar sus Hábitos de Alimentación. Centro para el control y prevención de enfermedades. Recuperado de: https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/spanish/losingweight/eatinghabits.html
12. Cuba, B. y Culqui, S. (2021). Conocimiento materno sobre higiene personal en preescolares, Alto Trujillo - El Porvenir [Tesis para optar titulo profesional de enfermería, Universidad Nacional de Trujillo]. Recuperado de: https://dspace.unitru.edu.pe/server/api/core/bitstreams/28e6f114-4695-4a2e-a5bc-8db10574c250/content
13. Defaz, P. (2017). Quiste complejo pélvico de origen anexial en paciente asintomática en atención primaria de salud [Trabajo académico de licenciatura, Universidad Técnica de Ambato]. Repositorio institucional. https://repositorio.uta.edu.ec/handle/123456789/25461
14. Delgado Ramos, M. (2020). “Comparación de la sensibilidad de escalas de dolor postoperatorio CHEOPS vs EVA en pacientes pediátricos de 4 a 7 años [Tesis de licenciatura, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla]. Repositorio institucional. https://repositorioinstitucional.buap.mx/items/c3f177a8-844f-402c-9658-f7b123e552fe
15. Diaz Mena, F.I. y Flores Castro, A.J. (2021). Dolor agudo en el servicio de urgencias. Revista Médica Sinergia, 6(11).https://revistamedicasinergia.com/index.php/rms/article/view/733
16. Gobierno Vasco (22 de febero de 2022). Plan estratégico de subvenciones del Departamento de Salud para el ejercicio 2022. Euskadi.eus. Recuperado de: https://www.euskadi.eus/otro_anuncio/orden-25-febrero-2022-consejera-salud-que-se- aprueba-plan-estrategico-subvenciones-del-departamento-salud-ejercicio-2022/web01- tramite/es/
17. Ferran Reinosos, D. J. (Febrero de 2021). El dolor. Umbral del dolor. Novedades de tratamiento en pacientes con dolor. NPunto, IV(5). https://www.npunto.es/revista/35/el-dolor-umbral-del-dolor-novedades-de-tratamiento-en-pacientes-con-dolor
18. García Romero, J., Jiménez Romero, M., -Fernandez Abasca, Fernández-Abascal Puente, Sanchez Castillo, F. y Gil fernandez, M. (2022). La medición del dolor: una puesta al día. Medicina Integral, 39(7), 317-320. https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-medicina-integral-63-articulo-la-medicion-del-dolor-una-13029995
19. García-Galicia, A., Guzmán-Maya, I., Montiel-Jarquín, Á. J., Parra-Salazar, J. A., González- López, A. M. y Loría-Castellanos, J. (2021). Validación de una escala facial de dolor en pacientes geriátricos posquirúrgicos. Cirugía y cirujanos, 89 (2). https://doi.org/10.24875/CIRU.20000094
20. Gómez Viana, L., Zepeda Blanco, C., Morán Álvarez, Á. y Cid Manzano, M. (2022). Manejo de las infecciones de la herida quirúrgica. Recuperado de: http://clinicainfectologica2hnc.webs.fcm.unc.edu.ar/files/2018/03/Manejo-de-las-infecciones-de-la-herida-quir%C3%BArgica.pdf
21. González Castañeda, F. (2022). “Discordancia entre diagnóstico histopatológico intraoperatorio y definitivo de masas anexiales en el hospital central Dr. Ignacio Morones Prieto [Trabajo académico de titulación, Universidad Autónoma de Potosí]. Repositorio institucional. http://ninive.uaslp.mx/xmlui/handle/i/7593
22. Gonzáles-Menocal, O., Armas-Pérez, B. y Ródriguez-Sánchez, E. (2019). Quiste de ovario torcido: a propósito de nuevos casos. Rev. Arch Med Camagüey, 23(5). http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1025-02552019000500661
23. Gutiérrez Moreno, M., Morales Chaves, R. y Valverde Solano, S. (Abril de 2023). Generalidades de sepsis del sitio quirúrgico. Revista Médica Sinergia, 8(4). https://revistamedicasinergia.com/index.php/rms/article/view/1023
24. Herdman, T., Kamitsuru, S. y Takáo Lopes, C. (2021). Diagnósticos enfermeros. Definiciones y Clasificación (1ra. ed.). ELSEVIER.
25. Hidalgo, L., Gonzales, M. y Salinas, C. (2019). Agentes relacionados a infección de sitio operatorio en adultos mayores pos operados en el Centro Médico Naval, 2013 – 2017. Revista de la Facultad de Medicina Humana, 19(3). http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2308-05312019000300007
26. Kaufer-Horwitz, M. y Pérez Hernández, J. F. (04 de Abril de 2022). La obesidad: aspectos fisiopatológicos y clínicos. Interdisciplina, 10(26), 1-29. https://www.revistas.unam.mx/index.php/inter/article/view/80973
27. León, M., Flores, J. y Zapata, D. (2022). Enfermería en el control el dolor agudo mediante terapias alternativas [Tesis de título profesional, Universidad Nacional de Chimborazo ]. Repositorio institucional. http://dspace.unach.edu.ec/handle/51000/9366
28. López Delgado, N. (2021). Guía Estilos de vida saludables. Recuperado de: https://www.medellin.gov.co/irj/go/km/docs/pccdesign/SubportaldelCiudadano_2/PlandeDesarrollo_0_19/ProgramasyProyectos/Shared%20Content/Estilos%20de%20vida%20saludable/Gu%C3%ADa%20Estilos%20de%20Vida/Gui%CC%81a%20Estilos%20de%20vida%20saludables.pdf
29. Maria-Josep Divins (Noviembre de 2023). Analgésicos. ELSEVIER, 29(6), 17-21. https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista- farmacia-profesional-3-articulo-analgesicos- X0213932415442083
30. Martínez Garduño, M., García-Ferrer, V., Gómez-Torres, D. y Angeles-Avila, G. (22 de Mayo de 2022). Cuidado de enfermería para la prevención de infección en. Revista Salud y Cuidado, 1(3). https://revistasaludycuidado.uaemex.mx/article/view/19050
31. MINSA (2021). Protocolo: Estudio de prevalencia de infecciones intrahospitalarias. Lima. Recuperado de: https://www.dge.gob.pe/portal/docs/tools/protocolo_iih.pdf
32. Miranda-Limachi, K., Rodríguez-Núñez, Y. y Cajachagua-Castro, M. (2019). Proceso de Atención de Enfermería como instrumento del cuidado, significado para estudiantes de ultrimo curso. Enfermería universitaria, 16(4). https://doi.org/10.22201/eneo.23958421e.2019.4.623
33. Moorhead, S., jhonson, M., Maas, M. L. y Swanson, E. (2018). Clasificación de Resultados de Enfermeria (NOC) (6ta ed.). Elsevier.
34. Mora, M. y Valle, R. (2016). Manejo de masas anexiales. Revista Clínica de la Escuela de Medicina de la Universidad de Costa Rica, 6 (1). https://www.medigraphic.com/cgi-bin/new/resumen.cgi?IDARTICULO=63863#:~:text=El%20manejo%20de%20una%20masa,y%20edad%20de%20la%20paciente.
35. Morocho Ruiz, J. D. y Llallahui Huamani, W. (2022). Educación y obesidad en el Perú: 2013- 2021 [Tesis de maestría, Universidad del Pacífico]. Repositorio institucional. https://repositorio.up.edu.pe/handle/11354/3750
36. Nazar, C., Coloma, R., Ignacio Contreras, J., Molina, I. y Fuentes H., R. (Diciembre de 2018). Consideraciones perioperatorias en el paciente obeso. Revista Chilena de Cirigía, 70(6). http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/s0718-40262018000600580
37. OMS (25 de Enero de 2020). Prevención y control de infecciones durante la atención sanitaria de casos en los que se sospecha una infección por el nuevo coronavirus (nCoV). Recuperado de: https://www3.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_docman&view=download&alias=51729-prevencion-y-control-de-infecciones-durante-la-atencion-sanitaria-de-casos-en-los-que-se-sospecha-una-infeccion-por-el-nuevo-coronavirus-ncov&category_slug=materiales-cientificos-tecnicos-7992&Itemid=270&lang=es
38. OMS (09 de junio de 2021). Obesidad y sobrepeso. https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
39. OMS (05 de Mayo de 2022). Lavarse las manos salva vidas: Tipos y técnicas de asepsia. Recuperado de: https://www.umanresa.cat/es/comunicacion/blog/lavarse-las-manos-salva-vidas-tipos-tecnicas-asepsia
40. Ramirez, J. y Rengifo, L. (2019). Torsión Anexial, Manejo Laparoscópico: Revisión De 2 Casos. Revista médica, Clínica del country, 10(1).
41. Reinoso, J., Rojas, M., Cherrez, L., & Guale, L. (2022). Infecciones asociadas a la atención en salud: un desafío para la salud pública. Revista Multidisciplinar, 6(6). https://doi.org/10.37811/cl_rcm.v6i6.3849
42. Reyna-Villasmil, E., Torres-Cepeda, D., & Rondon-Tapia, M. (2020). Hiperreacción luteínica durante el tercer trimestre del embaraz. Reporte de caso. Revista Peruana de Ginecología y Obstetricia, 66(1). http://dx.doi.org/10.31403/rpgo.v66i2239
43. Rodríguez Nájera, G., Camacho Barquero, F. A., & Umaña Bermúdez, C. A. (Abril de 2020). Factores de riesgo y prevención de infecciones del sitio quirúrgico. Revista Médica Sinergia, 5(4).
44. Rodríguez Fernández, Z., Fernández López, O., Ochoa Maren, G. y Romero García, L.I. (2017). Algunas consideraciones sobre las infecciones posoperatorias. Revista Cubana de Cirugía, 56(2). http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-74932017000200005
45. Ruiz-Romero, M.V., Guerra-Martín M.D., Alvarez-Tellado, L., Sanchez-Villar E., Arroyo Rodríguez A. y Sánchez-Gutierrez, M.C. (21 de junio de 2021). Terapias no farmacológicas para el dolor crónico no oncológico: percepciones de los pcientes. Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra, 44 (1). https://recyt.fecyt.es/index.php/ASSN/article/view/82312/64868
46. Tiscar Gonzáles, V., Menor Rodríguez, M., Rabadán Sainz, C., Fraile Bravo, M., Grupo Life, Styche, T., Valenzuela Ocaña, F.J., Muñoz García, L. (2020). Eficiencia de un apósito innovador en la cura de heridas: reducción de la frecuencia de cambio y del coste semanal por paciente. Gerokomos, 31 (1). https://dx.doi.org/10.4321/s1134- 928x2020000400001
47. Vera Carrasco, O. (2021). Aspectos farmacologicos para el uso racional de antibioticos. Revista Médica La Paz, 27(2). http://www.scielo.org.bo/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1726-89582021000200058
48. Vicente-Herrero, M.T., Delgado-Bueno, S., Bandrés-Moyá, F., Ramírez-Iñiguez-de-la-Torre, M.V., & Capdevilla-García, L.. (2018). Valoración del dolor. Revisión comparativa de escalas y cuestionarios. Revista de la Sociedad Española del Dolor, 25(4), 228-236. https://dx.doi.org/10.20986/resed.2018.3632/2017
49. ISWCAP (2020). ¿Qué es una complicación de una herida quirúrgica?. Recuperado de: https://iswcap.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/LA-IDENTIFICACION-Y-PREVENCION.pdf
50. Yagui Moscoso, M., Vidal-Anzardo, M., Rojas Mezarina, L. y Sanabria Rojas, H. (2021). Prevención de infecciones asociadas a la atención de salud: conocimientos y prácticas en médicos residentes. Anales de la Facultad de Medicina, 82(2), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.15381/anales.v82i2.19839
51. Zila-Velasque, J. P., Grados-Espinoza, P., Regalado-Rodríguez, K. M., Luna-Córdova, C. J., Calderón, G. S. S., Díaz-Vargas, M., Sifuentes-Rosales, J. y Diaz-Vélez, C. (2022). Prevalencia y factores del trastorno de conducta alimentaria en estudiantes de medicina humana del Perú en el contexto de la pandemia de covid-19: estudio multicéntrico. Revista colombiana de psiquiatría. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcp.2022.07.005
FINANCING
There is no funding for this work.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Vilma L. Chumpitaz-Saravia, Blanca Villaverde-Saravia, Sofía D. Vivanco-Hilario, Wilter C. Morales-García.
Research: Vilma L. Chumpitaz-Saravia, Blanca Villaverde-Saravia, Sofía D. Vivanco-Hilario, Wilter C. Morales-García.
Methodology: Vilma L. Chumpitaz-Saravia, Blanca Villaverde-Saravia, Sofía D. Vivanco-Hilario, Wilter C. Morales-García.
Project administration: Vilma L. Chumpitaz-Saravia, Blanca Villaverde-Saravia, Sofía D. Vivanco-Hilario, Wilter C. Morales-García.
Drafting - original draft: Vilma L. Chumpitaz-Saravia, Blanca Villaverde-Saravia, Sofía D. Vivanco-Hilario, Wilter C. Morales-García.
Writing-revision and editing: Vilma L. Chumpitaz-Saravia, Blanca Villaverde-Saravia, Sofía D. Vivanco-Hilario, Wilter C. Morales-García.
ANNEXES
Appendix A: Care plans
|
Diagnosis nurse |
Planning |
Execution |
Evaluation |
||||||
|
Domain:12 Comfort Class 1: Physical comfort Diagnosis: Acute pain (00132) related to damaging agent physical injury associated with operative wound as evidenced by expression of facial, verbalization of pain and rating of 6/10 on Eva's scale |
Results and Indicators |
Baseline score (1-5) |
Target score |
Interventions activities |
|
Final score |
Score of change |
||
|
Result NOC: Pain level (2102) |
2 |
Maintain at |
NIC: Acute pain management (1410) |
M |
T |
N |
4 |
+2 |
|
|
Increase to: 4 |
|||||||||
|
Scale: Serious (1) None (5) |
|
|
Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indicators: |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Referred pain |
2 |
|
Perform a comprehensive pain assessment, which include the location |
|
|
|
5 |
Refers to a decrease in the pain |
|
|
Facial expression of pain |
2 |
|
Identify the intensity of the pain |
|
|
|
4 |
No facial expression of pain |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Concern |
2 |
|
Ask the patient about the level of pain assessed on Eva scale |
|
|
|
4 |
Mild, tolerable pain |
|
|
Muscle tension |
2 |
|
Administration of analgesic according to medical prescription. |
|
|
|
4 |
Partially effective analgesic for pain |
|
|
Administering interventions according to the patient's preferences. |
|
|
|
|
Antalgic position |
||||
|
Nursing diagnosis |
Planning |
Execution |
Evaluation |
||||||
|
Domain:11 Security and Protection Class: 1 (00004) Risk of infection in the surgical wound as it is evidence by the obesity, associated with invasive procedure and drain pen rose to colostomy bag. |
Results and Indicators |
Score basal (1-5) |
Score diana |
Interventions activities |
|
Score end |
Score of change |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
NOC result Knowledge of infection control (1842) |
3 |
Keep in |
Intervention: NIC Protection against infections (6550) |
M |
T |
N |
4 |
+1 |
|
|
Increase to: 4 |
|||||||||
|
Scale: No knowledge (1) knowledge extensive (5) |
|
|
Activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indicators: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms of infection |
2 |
|
Observe them signs and symptoms of infection systemic and located |
|
|
|
4 |
Wound tissue operation without sign of alteration. |
|
|
Procedure infection control |
3 |
|
Observe the vulnerability of the patient to the infections |
|
|
|
4 |
The staff practices the measures of biosecurity Receives the antibiotic prophylactic indicated |
|
|
Importance of the hygiene of hands |
3 |
|
Manage the antibiotics indicated: clindamycin and ceftriazone, complying with the five correct |
|
|
|
4 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Body temperature monitoring every 6 hours |
|
|
|
|
Stable body temperature |
|
Maintain asepsis at all times procedure |
|
|
Decrease in the transmission of microorganisms. |
||||||
|
Nursing diagnosis |
Planning |
Execution |
Evaluation |
||||||
|
Domain:2 Nutrition Class: 1 (00232) Obesity related to consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages and fried food intake and abnormal patterns of conduct morbid obesity with BMI > 41%. kg/m2 |
Results and Indicators |
Baseline score (1-5) |
Target score |
Interventions activities |
|
Final score |
Change score |
||
|
NOC result State nutritional (1004) |
2 |
Keep in Increase to: 4 |
Intervention: NIC Nutritional counseling 5246) Activities |
M |
T |
N |
3 |
+1 |
|
|
Scale: 1 Severe deviation from normal range (1) to No deviation from the range normal (5) |
|
Assist in identification of desired eating behaviors change. |
|
|
|
|
Identifies healthy foods |
||
|
Indicators: |
|
|
Establish enforceable goals short, medium and long term for the change of the nutritional status. |
|
|
|
|
Establish status nutritional in the medium term |
|
|
Nutrient intake |
2 |
Facilitate attention by a nutrition professional for information about the need for dietary modification by health reasons (loss of weight) |
|
|
|
3 |
Consume a low-sodium, low-fat diet and vegetables. |
||
|
|
Ingestion of food |
3 |
|
Participate with the patient in the measurement fluid intake and elimination, blood pressure readings, fluid intake elimination, blood weight every day. |
|
|
|
2 |
Consumes three meals per day |
|
Weight/height ratio |
2 |
|
Provide information about the need for dietary modification based on weight loss, fluid intake and diet. recommended |
|
|
|
3 |
Obesity III |
|
Appendix B: Nursing Assessment

Appendix C: Informed Consent
Universidad Peruana Union Graduate School
UPG of Health Sciences.
Informed Consent Purpose and procedures
I have been informed that the present study has the objective of determining the role of nurse in the care of the post-surgical patient of adnexal cystectomy in the Gynecological Obstetrics Service of a national hospital in Chincha. This academic work is carried out by Vilma Leonor Chumpitaz Saravia and Blanca Gloria Franco Villaverde, under the advice of our course teacher. The information provided through the assessment guide, interview and physical examination will be confidential and will be used only for the purposes of the study.
Risks of the study
I have been told that there is no physical, chemical, biological, and psychological risk associated with this academic work. But since some personal information will be obtained, there is the possibility that my identity may be discovered from the information given. However, precautions such as identification by numbers will be taken to minimize such a possibility.
Benefits of the study
There is no monetary compensation for participation in this study.
I have been informed that my participation in the study is completely voluntary and that I have the right to withdraw my consent at any point before the report is finalized, without penalty. The same applies for my initial refusal to participate in this project.
Having carefully read the consent form and having listened to oral explanations of the investigator, I voluntarily sign the present document.
First and Last name: G. A. C
DNI: Date: 07-10-2022
Signature
Appendix D: Evaluation scale
Scale of normal temperature levels
Scale of body mass index values
Scale of hemoglobin values
Blood glucose value scale
Levels from respiratory rate
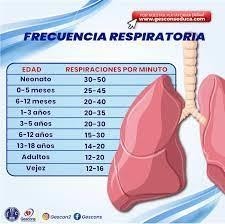
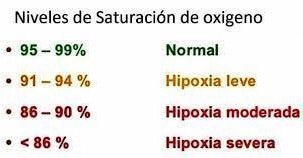
Blood pressure levels
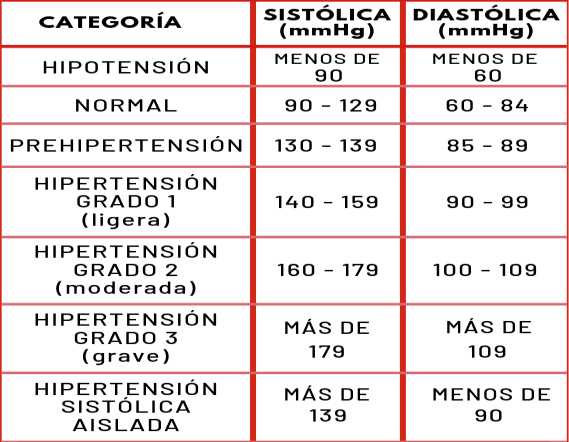
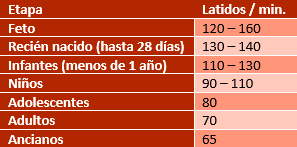
Heart rate levels per minute
Pain Rating Scale